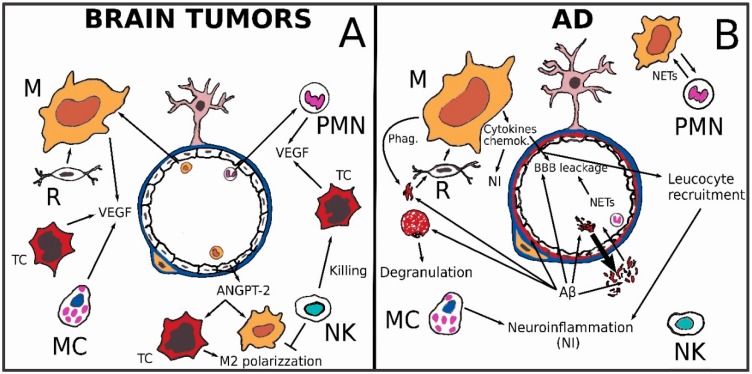
Figure 3.
(A) The structure of neoformed vessels in most important brain tumors, such as glioblastoma, is often abnormal with permeability of BBB. VEGF is the major angiogenetic factor: it can be produced by cancer cells (mainly in hypoxic areas), MCs, PMNs and Macrophages. VEGF acting on TJs proteins synthesis, can enhance vessels permeability. Endothelial angiopoietin (ANGPT2) promote the recruitment of proangiogenic, M2-polarised macrophages. In endothelial cells the Ang/Tie pathway can regulate pathological vascular remodeling and vascular permeability during the processes of inflammation, tumor angiogenesis and metastasis. The same pathway can also be activated in macrophages and cancer cells. NK cells in GBM may exert a preferential killing activity of GBM stem-like cells. NK cells, by cytokine secretion, could be able to exchange TAMs polarization from anti-inflammatory to pro-inflammatory phenotype; (B) In subjects affected by sporadic Alzheimer’s disease (AD) Aβ amyloid accumulation is due to a reduced clearance from the brain, ascribable to reduced metabolism, diminished efflux across the BBB or decreased CSF bulk flow through glymphatic system. Both brain-derived and peripheral Aβ amyloid are transported through BBB by receptor-mediated transcytosis. Microglial cells can be activated by Aβ fibrils interacting with several receptors, thus inducing the production of pro-inflammatory mediators. Neutrophil Extracellular Traps (NETs) are fibers of decompacted chromatin decorated with antimicrobial proteins and histones originating from PMNs that can contribute to the activation of microglia and BBB leakage. Aβ amyloid causes MCs degranulation contributing also in such a way to neuroinflammation (NI).