FIG 2.
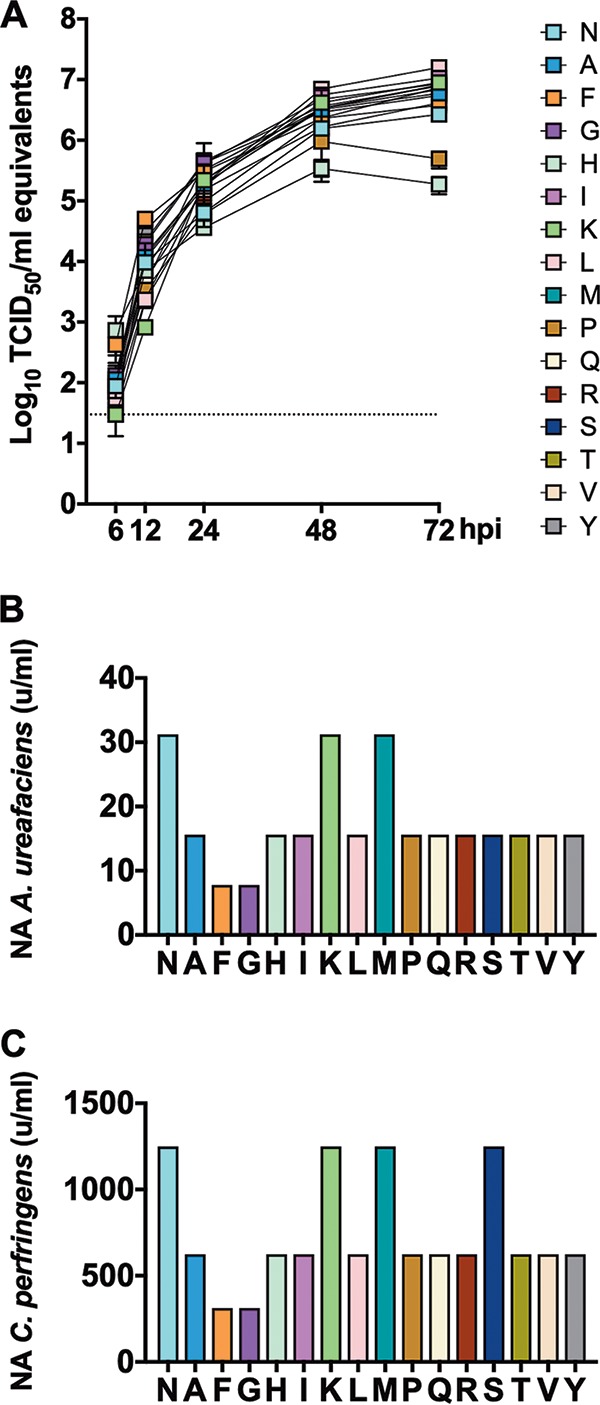
Substitutions at residue 145 show no major impact on virus growth but decrease receptor binding avidity. (A) Confluent monolayers of MDCK cells were inoculated with H3 viruses carrying amino acid substitutions at residue 145 at an MOI of 0.01 and incubated at 37°C. At 6, 12, 24, 48, and 72 hpi, tissue culture supernatants from inoculated cells were collected for virus RNA quantification by rRT-PCR, which was expressed as log10 TCID50/ml equivalents. Plotted data represent means ± standard deviations (SD). (B and C) Turkey red blood cells pretreated with different amounts of neuraminidase from either Clostridium perfringens (B) or Arthrobacter ureafaciens (C) were mixed with H3 viruses carrying amino acid substitutions at residue 145 to quantify virus agglutination as a measure of virus binding avidity. Data are expressed as the maximal amount of neuraminidase that allowed full agglutination. Panels B and C show representative data of one out of two and three independent experiments, respectively, with samples run in duplicates in each experiment. Plotted data represent means ± standard deviations (SD).
