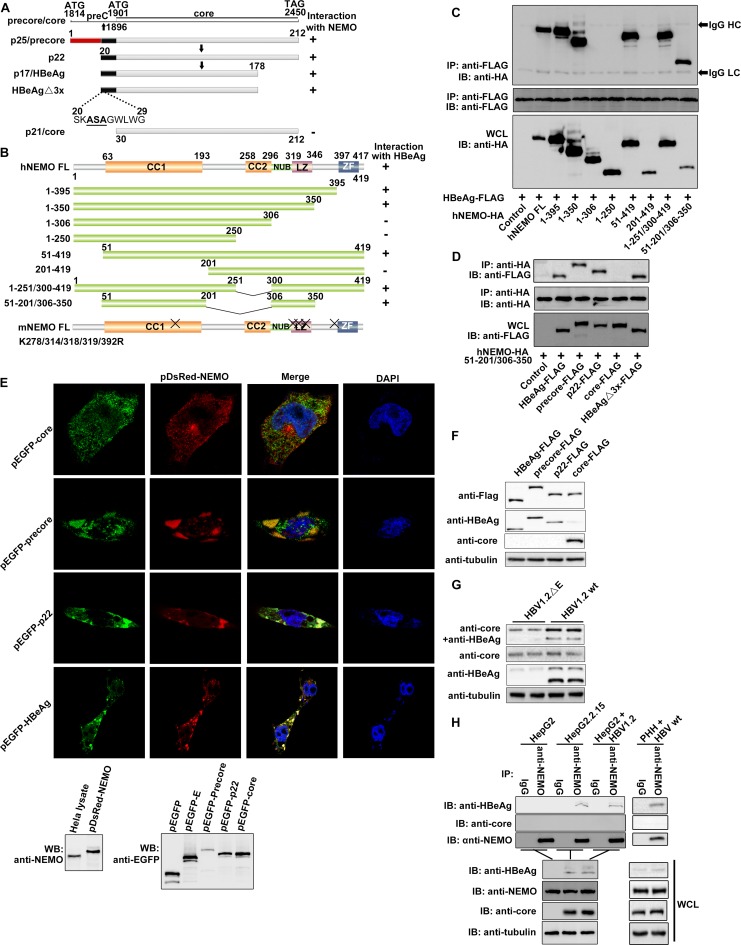
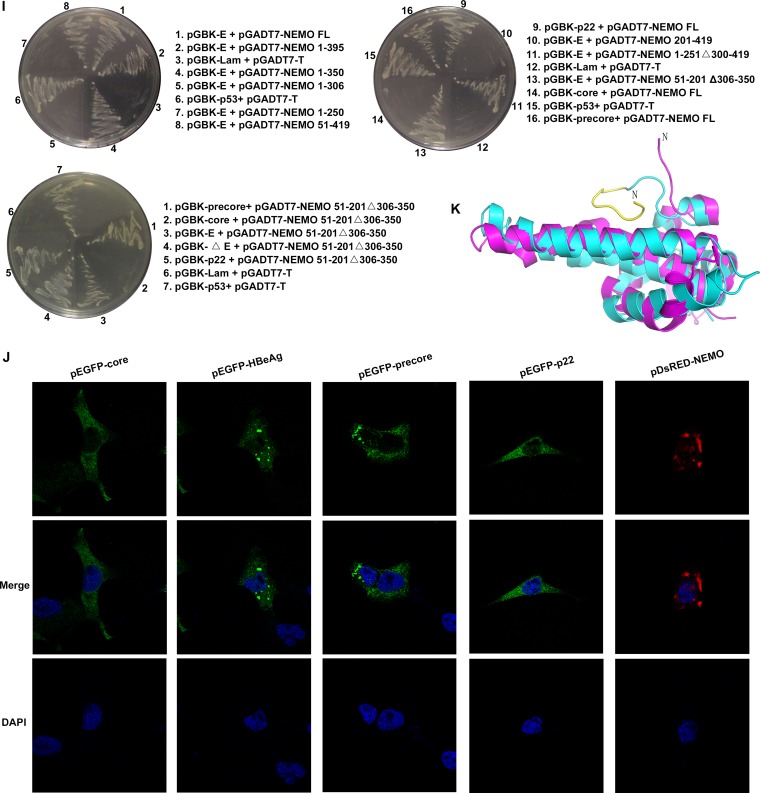
FIG 1.
Specific interactions of NEMO with HBeAg and its precursor proteins, precore and p22. (A and B) Schematic drawings of NEMO, HBeAg and its precursors, and their derivatives used in this work. CC1, coiled-coiled domain 1; CC2, coiled-coil domain 2; LZ, leucine zipper; ZF, zinc finger; NUB, ubiquitin binding. “X” indicates the sites of mutagenesis described in the text. (C and D) HEK 293T cells were cotransfected with plasmids as indicated, and coimmunoprecipitation (co-IP) and Western blotting (WB) were performed according to standard protocol mentioned in Materials and Methods. WCL, whole-cell lysate; HC, IgG heavy chain; LC, IgG light chain. (E) HeLa cells were cotransfected with plasmids for pDsRed-NEMO and pEGFP-HBeAg plus their precursors. Nuclear localization was detected using DAPI. Orange signals reveal the specific associations (upper portion). Expressions of NEMO and HBeAg plus its precursors were also confirmed via immunoblotting using anti-enhanced green fluorescent protein (anti-EGFP) and anti-NEMO antibodies, respectively (lower portion). (F and G) HEK 293T cells were cotransfected with plasmids as indicated, and Western blotting was performed by using the proper antibodies as indicated. (H) Interaction of endogenous HBeAg and NEMO was examined when HepG2 cells were cotransfected with plasmids as indicated or primary human hepatocytes (PHHs) were incubated with wild-type HBV and cultured for 8 days. Cells were then harvested and analyzed via co-IP and WB. HepG2.2.15 cells were used as positive controls. (I) The yeast two-hybrid system was used to determine the domains necessary for the interaction of NEMO and HBeAg. (J) Locations of NEMO, HBeAg, and its precursors in HeLa cells. HeLa cells were transfected with the indicated plasmids. Nuclear localization was detected using DAPI. (K) Superimposition of structures of HBeAg (cyan; PDB code 3V6Z) and HBV core (magenta; PDB code 5WTW); residues 20 to 30 of HBeAg (which core lacks) are shown in yellow. N, N terminus.