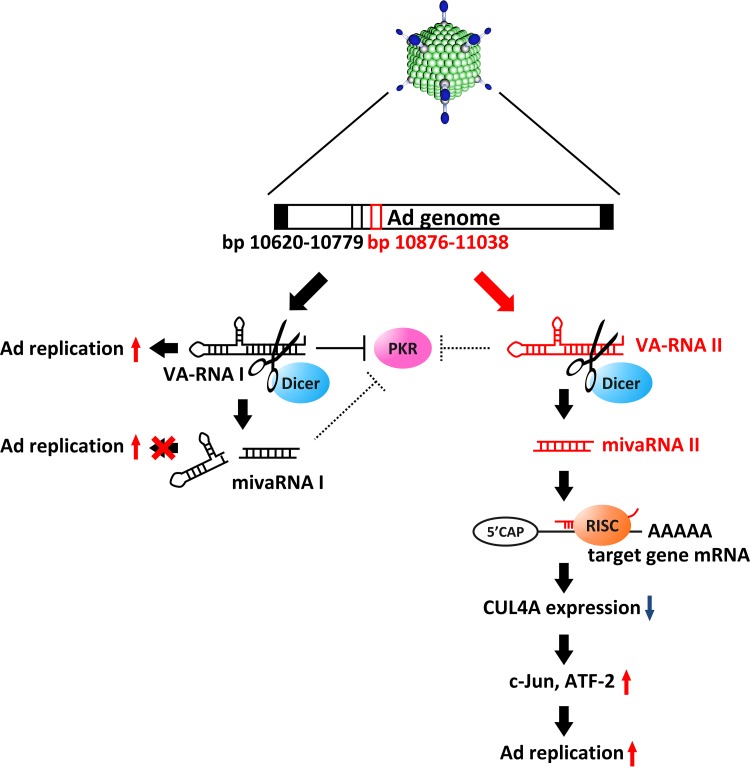
FIG 7.
Model of VA-RNAII-mediated promotion of Ad replication via posttranscriptional gene silencing of CUL4A. After Ad infection, VA-RNAI and -II are rapidly transcribed and promote Ad infection in different ways. VA-RNAI inhibits the activation of PKR, which plays a key role in antiviral responses. VA-RNAII functions as a precursor of mivaRNAII, which promotes Ad infection, while mivaRNAI does not support Ad infection. Suppression of CUL4A, the highest-potential target of mivaRNAII, amplifies JNK signaling via stabilization of c-Jun and ATF2, leading to promotion of Ad replication.