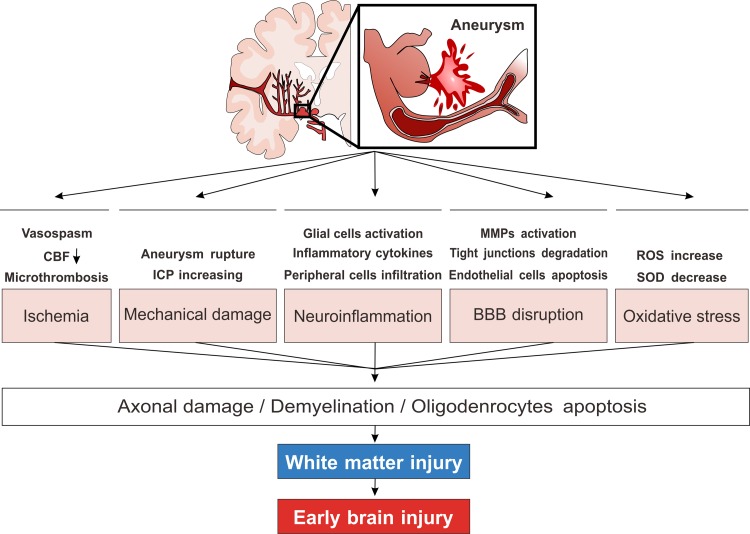
Fig. 1.
Simplified schematic diagram of the possible pathophysiological mechanisms of WMI following SAH. Vasoconstriction induced CBF decrease, aneurysm rupture, and ICP increase induced mechanical barotrauma are both responsible for the WMI in EBI after SAH. Later on, BBB disruption characterized by MMPs activation and endothelial cells apoptosis, neuroinflammation characterized by glial cells activation, peripheral inflammatory cell infiltration and cytokines release, oxidative stress will further deteriorate WMI. Although the detailed molecular mechanisms remain unclear, these mechanisms will finally lead the consequence of oligodendrocytes apoptosis, white matter demyelination and axonal damage. SAH: subarachnoid hemorrhage; CBF: cerebral blood flow; WMI: white matter injury; MMPs: matrix metalloproteinase; ICP: intracranial pressure.