Figure 1. Peroxisomal matrix and membrane protein import in yeast (an overview).
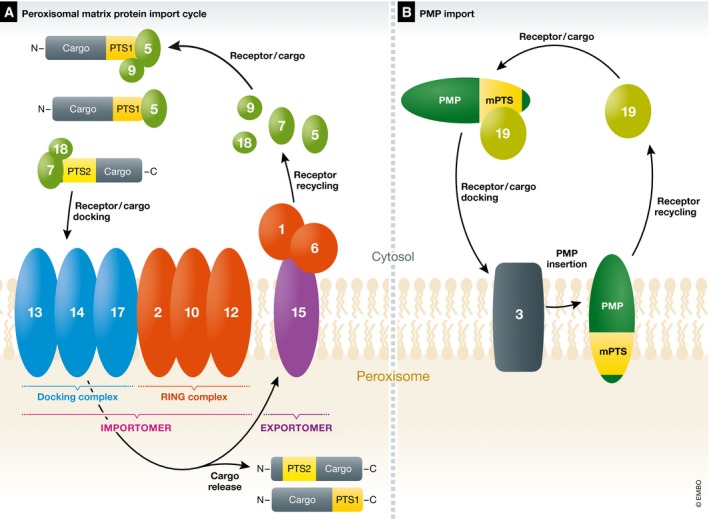
Most proteins destined for import into the peroxisome matrix possess either a C‐terminal PTS1 or an N‐terminal PTS2. (A) The peroxisomal matrix protein import cycle. These cargos synthesized in the cytosol are recognized by PTS receptors, Pex5 for PTS1 and Pex7 for PTS2, respectively. Pex7 generally works with a co‐receptor (Pex18/21 in S. cerevisiae or Pex20 in P. pastoris only Pex18 is shown). Pex9 is a Pex5‐related protein found in S. cerevisiae that acts on limited PTS1 cargos as described in the text 10, 11. The PTS receptor/cargo complex, along with the co‐receptor, where applicable, docks at the peroxisome membrane with the docking complex, comprised of Pex13, Pex14, and Pex17. PTS cargos are translocated into the peroxisome matrix across translocons in the peroxisome membrane. The minimal translocon in yeast involves Pex14 and Pex5 for PTS1 import 12, and likely Pex14/Pex17 and Pex18 for PTS2 import 13. Associated with the docking complex is the RING subcomplex comprised of Pex2, Pex10, and Pex12 that have E3 ligase activities involved in ubiquitin‐dependent, PTS‐receptor recycling and QC steps (sections Brief overview of peroxisomal matrix protein import and QC during peroxisomal matrix protein import). Together, the docking and RING subcomplexes form the importomer complex 14, 15. Following PTS cargo release in the peroxisome lumen, the PTS receptors, and co‐receptors where applicable, recycle from the peroxisomes back to the cytosol for another round of import, using components collectively called the exportomer, whose components are described in the text 16. (B) The PMP import cycle for the direct import of proteins into the peroxisome membrane (section The direct import of PMPs to peroxisomes). Each PMP has at least one mPTS that is bound to, and the PMP is chaperoned by, Pex19, which docks at the peroxisomes via interactions with Pex3. The PMP is inserted into the membrane and Pex19 recycles back to the cytosol for another round of PMP import.
