Figure 5. Peroxisomal quality control pathways.
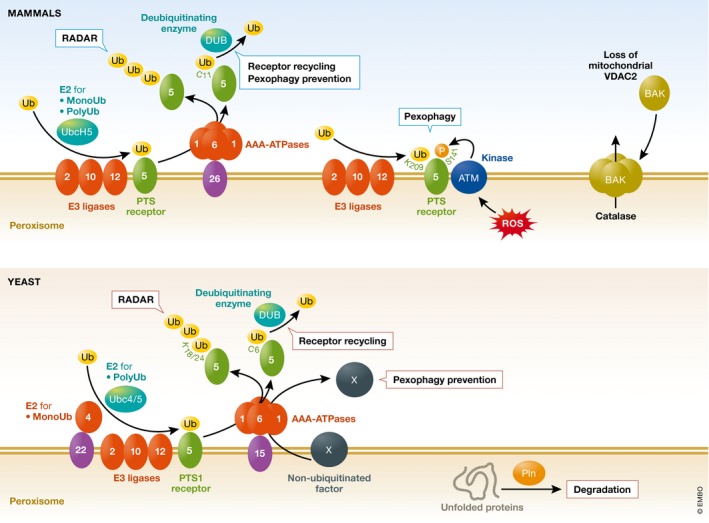
During peroxisomal matrix protein import, after the PTS receptor protein, Pex5, has released the cargo in the peroxisomal matrix, it follows different fates. Receptor Recycling: Mono‐ubiquitination (monoUb) of Pex5 occurs at a conserved cysteine residue (C6 in yeast and C11 in mammals) catalyzed by the E2‐enzyme complex (Pex4/Pex22) in yeast or UbcH5 in mammals, and the E3 ligases Pex2, Pex10, and Pex12 21. Next, mono‐ubiquitinated Pex5 is recycled to the cytosol, mediated by the AAA‐ATPases, Pex1, and Pex6 141. Finally, ubiquitin is removed by a deubiquitinating enzyme (DUB) and Pex5 becomes available for another round of import 24. RADAR: As a quality control mechanism, poly‐ubiquitination (polyUb) of Pex5 at conserved lysine residues in yeast by the E2‐enzyme Ubc4 and E3 ligases direct Pex5 for degradation by the proteasome (RADAR) 186. In mammals, the E2‐enzyme UbcH5 has been implicated in mono‐ and poly‐ubiquitination of PEX5. Pexophagy (and its prevention): As is the case in yeast, during receptor recycling in mammals, Pex1 and Pex6 are implicated in the recycling of PEX5, but in addition their presence prevents pexophagy 142. The mechanism in mammals is through recycling PEX5 from the peroxisomal membrane, as PEX5 is also target of ubiquitination which is recognized by autophagy factors driving pexophagy 186. For example, pexophagy is induced by high levels of peroxisomal reactive oxygen species (ROS), which recruits ATM to peroxisomes. ATM phosphorylates (P) PEX5 at Ser141 (S141), which then mediates the ubiquitination of PEX5 either at Lys209 (K209) 9. Alternatively, Cys11 is ubiquitinated 7. In yeast, the pexophagy prevention by the AAA‐ATPases is most probably independent of Pex5, which is not required for pexophagy. Instead, a different factor (X) that triggers pexophagy, which could be the yeast pexophagy receptor (Atg36), might need to be removed from the peroxisome surface by Pex1 and Pex6. Other QC mechanisms: The peroxisomal Lon type AAA‐protease, Pln, degrades damaged proteins in the peroxisomal matrix 182, 187, 188, 189. This protease is absent in S. cerevisiae but is present in other yeasts. Another QC mechanism may operate to recycle back to the cytosol damaged enzymes, which could be degraded by the proteasome. Such a mechanism has been described by the release of catalase to the cytosol by a peroxisome‐localized BAK, due to the lack of mitochondrial VDAC2, which normally retains BAK at mitochondria 179.
