Fig. 1. Regulation of YAP and the Hippo core.
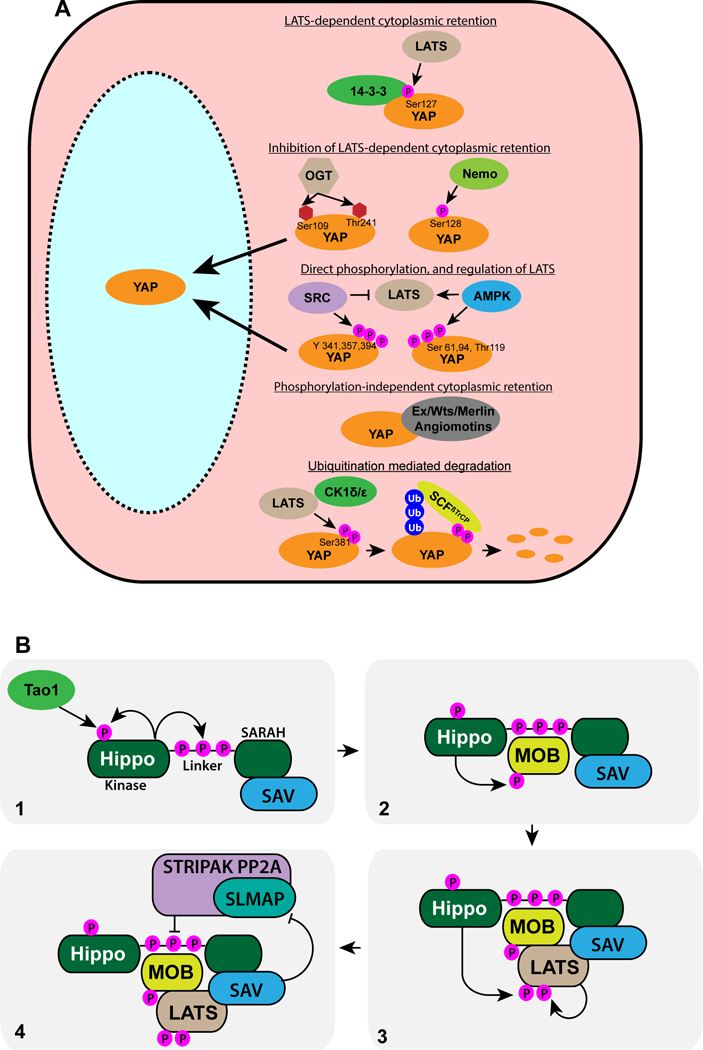
A) Several biochemical mechanisms that regulate YAP proteins, as described in the text, are shown. Amino acids modified in human YAP1 are indicated. OGT = O-N-acetylglucosaminyl transferase.
B) Sequence of interactions and phosphorylations involved in activation of LATS proteins, as described in the text, are shown. Hippo is activated by phosphorylation within its kinase domain, mediated by Hippo or Tao1 (1). Hippo phosphorylates Ser residues in its linker region, which recruits MOB, which is then phosphorylates by Hippo (2) Phosphorylated MOB recruits LATS (together with SAV and other pathway components not shown here), and LATS is then phosphorylated by Hippo, and also autophosphorylates to generate active LATS. This complex can be deactivated by SLMAP-mediated recruitment of the STRIPAK PP2a phosphatase complex (4); this recruitment is inhibited by SAV.
