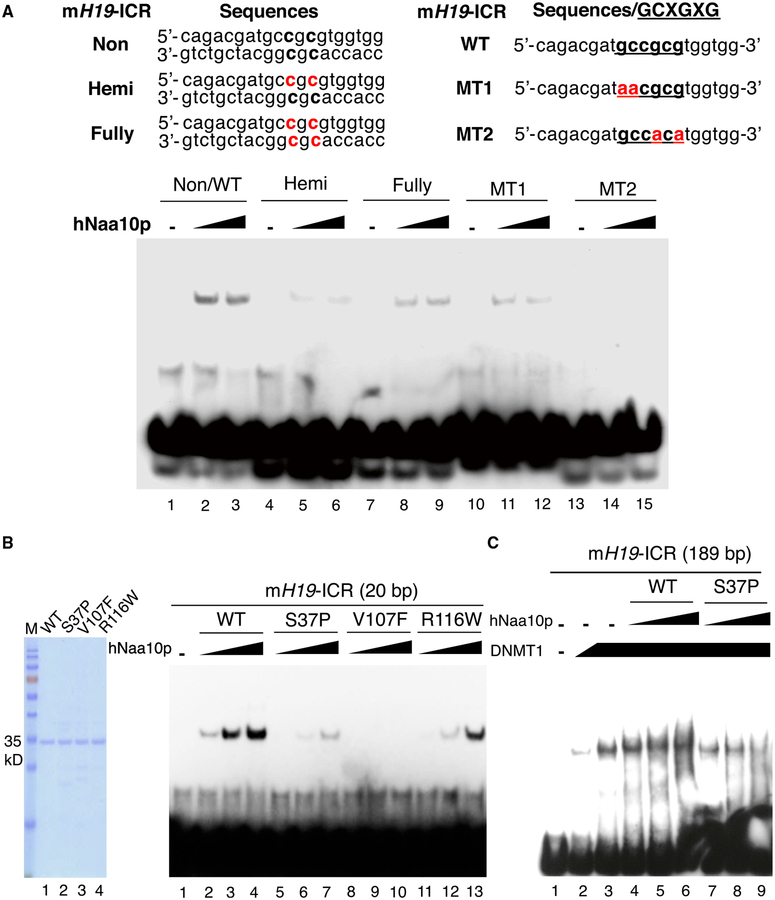
Figure 7. WT Naa10p, but Not the Human Disease-Associated Mutants, Directly Binds to the Non-methylated GCXGXG Motif of H19-ICR and Facilitates DNMT1 Binding.
(A) Naa10p preferentially binds to the non-methylated GCXGXG motif at H19-ICR. The binding of recombinant hNaa10p to the biotin-labeled 20-mer oligo of mouse H19-ICR with or without methylated cytosines or mutations (indicated in red) was analyzed by EMSA. hNaa10p amount: 2 μg (lanes 2,5,8,11, and 14) and 4 μg (lanes 3, 6, 9, 12, and 15).
(B) Clinically relevant mutations disrupt the binding of Naa10p to the H19-ICR fragment. Left: Coomassie blue staining of recombinant WT and mutant hNaa10p used for the EMSA. Right: EMSA of WT and mutant hNaa10p binding to the biotin-labeled 20-mer oligo of mouse H19-ICR. hNaa10p amount: 1 μg (lanes 2,5, 8, and 11), 2 μg (lanes 3, 6, 9, and 12), and 4 μg (lanes 4, 7, 10, and 13).
(C) WT Naa10p, but not the Ogden syndrome-relevant S37P mutant, facilitates DNMT1 binding to H19-ICR.The biotin-labeled 189-bp ChIP region of mouse H19-ICR was incubated in the absence (lane 1) or presence of recombinant human DNMT1 (Hashimoto et al., 2012) (lane 2,0.5 μg, and lanes 3–9,1 μg) with WT human Naa10p (lanes 4–6) or its S37P mutant (lanes 7–9) for EMSA. hNaa10p amount: 0.5 μg (lanes 4 and 7), 1 μg (lanes 5 and 8), and 2 μg (lanes 6 and 9).
See also Figure S7.