Figure 4 |. Connectivity between primary sensory, motor, dorsal attention, ventral attention, and cingulo-opercular communities mediate the relationship between connector hubs and modularity.
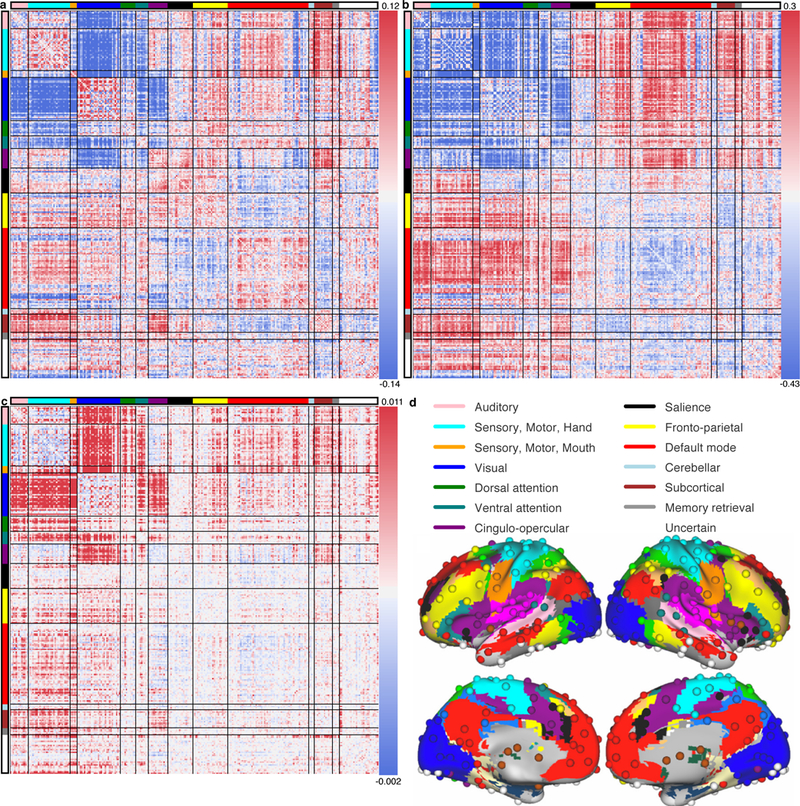
a, Each entry is the Pearson correlation coefficient, r, across subjects (N=476), between modularity (Q) and that edge’s weights. b, For each connector hub, the Pearson r between the hub’s participation coefficients and each edge’s weights across subjects (N=476) was calculated. The matrix in b is the mean of those matrices across connector hubs. c, To investigate the relationship between connector hubs’ participation coefficients, edge weights, and Q, a mediation analysis was performed for each connector hub, with an edge’s weights mediating the relationship between the connector hub’s participation coefficients and Q indices (N=476). Each edge’s mean mediation value between connector hubs’ participation coefficients and Q is shown. d, The anatomical locations of each node and community on the cortical surface36,49.
