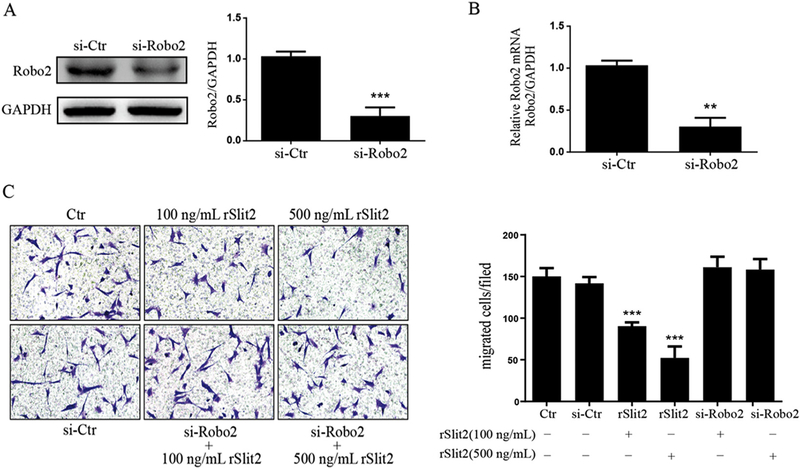
Fig. 6.
Slit2/Robo2 signaling inhibited HSCs migration. Transfection of Robo2 siRNA (si-Robo2) in JS1 cells efficiently decreased Robo2 protein and mRNA expression. (A) Representative Western blot profile of Robo2 protein level in Robo2 siRNA transfected JS1 cells is shown. Data are presented as the ratio of Semi-quantitative analyzed Robo2 signal to that of GAPDH. ***P < 0.001 compared to the control siRNA transfected cells (si-Ctr); (B) The mRNA expression of Robo2 were determined by real time quantitative PCR (RT-qPCR). The expression levels were normalized to GAPDH. Data are presented as mean ± SD of N = 3 per group in three independent experiments. **P < 0.01 compared to the control siRNA transfected cells (si-Ctr). (C) Representative pictures for the effect of rSlit2 (100 ng/mL and 500 ng/mL) with or without Robo2 siRNA knockdown (si-Robo2) on HSCs migration are shown. rSlit2 dose dependently inhibited JS1 cells migration. The inhibitory effect of rSlit2 on HSCs migration was abrogated by Robo2 siRNA knockdown. Magnification was 20×. Data are presented as mean ± SD of N = 3 per group in three independent experiments. ***P < 0.001 compared to si-Ctr.