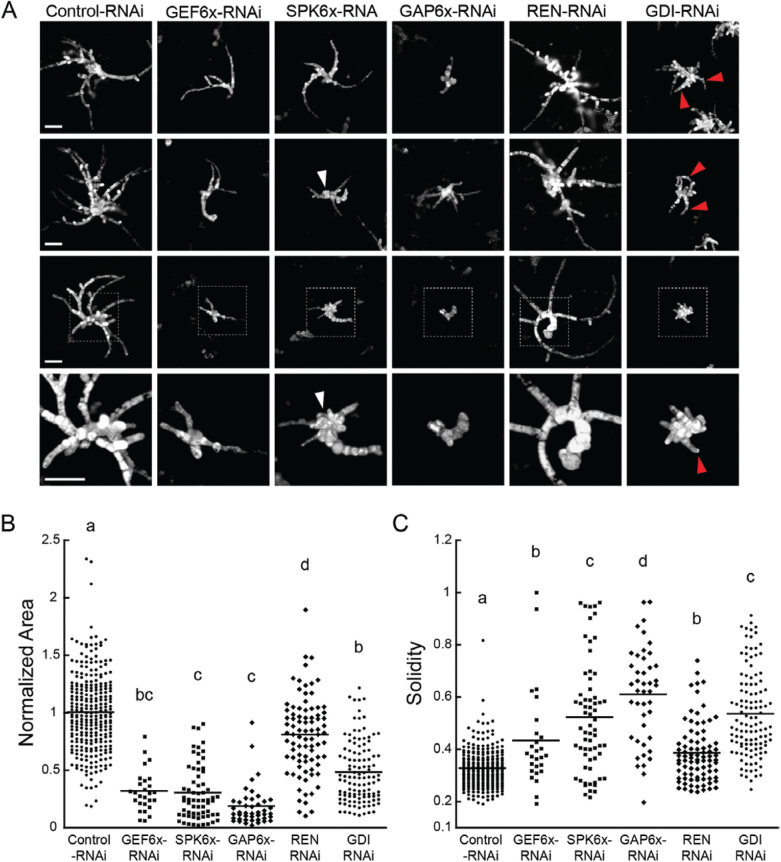
Fig. 2.
ROP regulators contribute differentially to polarized growth. (A) Representative images of chlorophyll autofluorescence from 7-d-old plants transformed with a construct silencing the indicated gene family. The images for each construct represent individual transformants and display areas similar to that of the average area for that construct (control, 275 plants from nine transformations; GEF6X-RNA, 27 plants from three transformations; SPK6X-RNAi, 65 plants from three transformations; GAP6X-RNAi, 44 plants from three transformations; REN-RNAi, 84 plants from three transformations; GDI-RNAi, 117 plants from three transformations). The regions indicated with boxes in the third row of images are shown in magnified view in the bottom row. Clusters of isotropic cells observed in SPK6x-RNAi plants and polarized extensions observed in GDI-RNAi plants are indicated with arrowheads. The scale bars for each row are 100 μm. (B) Quantification of plant area and solidity. Area is normalized to the average size of plants transformed with the control plasmid, and the means are indicated by horizontal lines. Different letters indicate groups with significantly different means as determined by ANOVA with a Tukey post hoc test (α=0.05).