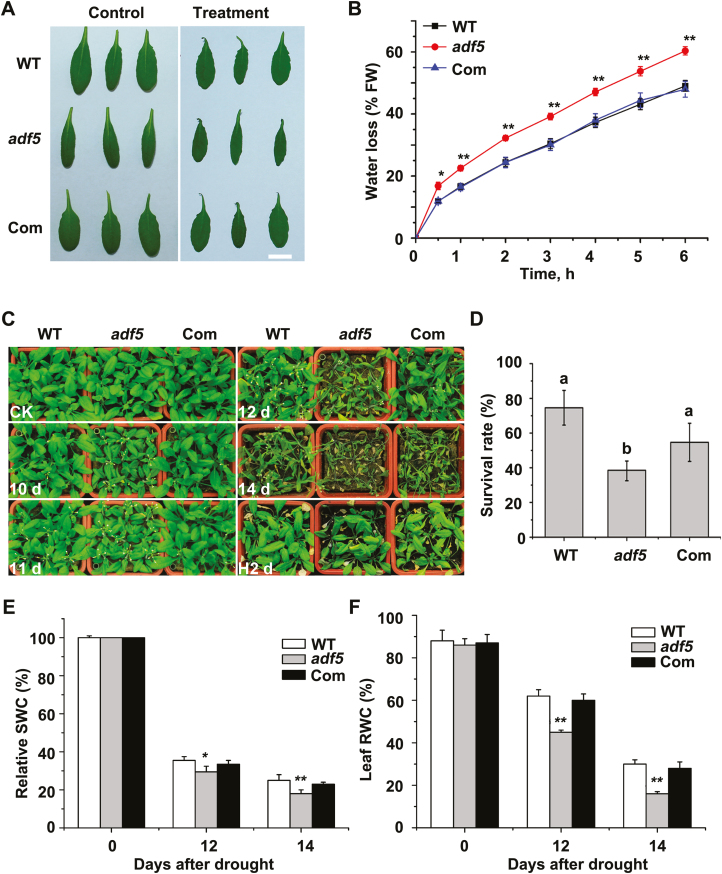
Fig. 2.
Mutation of ADF5 increases plants’ sensitivity to water deficit. (A) Leaves detached from WT, adf5, and Com Arabidopsis plants were placed on a bench for 0 h (control) and 6 h (treatment). Scale bar=1 cm. (B) Water loss of leaves detached from WT, adf5, and Com plants. Data presented are the mean ±SE of three independent experiments. *P<0.05, **P<0.01 (Student’s t-test). (C) Phenotypic comparison of WT, adf5, and Com plants grown in soil after water was withheld for different durations (10, 11, 12, and 14 days) and the plants were then rewatered for 2 days. Three independent experiments were performed that yielded similar results. (D) Plant survival rate after rewatering for 3 days. Different letters above the bars represent significant (P<0.05) differences (Student’s t-test). Data presented are the means ±SEs of three independent experiments. (E) Relative soil water content (SWC) after withholding water for different durations. Data presented are the mean ±SD of three independent biological replicates. *P<0.05, **P<0.01 (Student’s t-test). (F) Leaf relative water content (RWC) after withholding water for different durations. Data presented are the mean ±SD of three independent biological replicates. **P<0.01 (Student’s t- test).