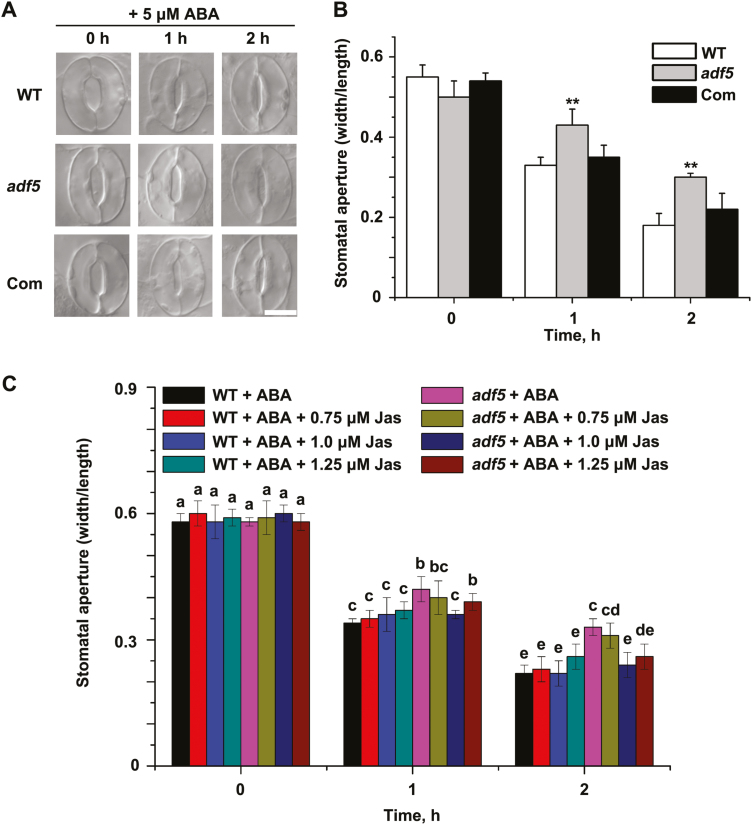
Fig. 3.
The adf5 mutation impairs ABA-mediated stomatal closure. (A) Representative images of WT, adf5, and Com stomata showing stomatal closure in response to ABA treatment. (B) Quantification of stomatal closure in WT, adf5, and Com plants in response to 5 μM exogenous ABA; the stomatal aperture is indicated as the ratio of stomatal width/length. Data presented are the mean ±SE of three independent biological replicates. Significant differences in comparison with the WT are indicated as *P<0.05, **P<0.01 (Student’s t-test). (C) Jasplakinolide (Jas) partially rescued the stomatal sensitivity of adf5 plants to ABA. The stomatal apertures were measured at the indicated times. Data presented are the mean ±SE of three independent biological replicates; different letters above the bars indicate significant (P<0.05) differences.