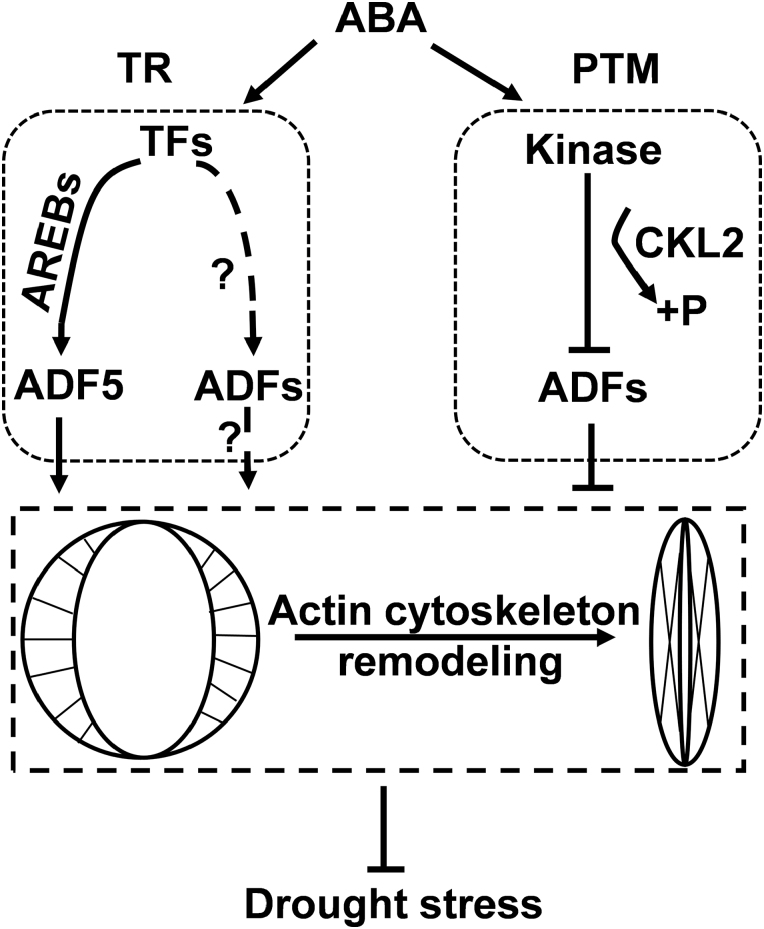
Fig. 8.
A working model for ADFs involved in the regulatory network between ABA signaling and actin cytoskeleton remodeling. ABA/drought activates downstream kinases such as CKL2, which phosphorylate ADFs (ADF1/2/3/4) and repress their actin severing/depolymerizing activity. This cascade disrupts actin cytoskeleton dynamics and subsequently inhibits stomatal closure via post-translational modification (PTM). Transcriptional regulation (TR) may be complementary to the ABA signaling pathway for the activity of ADFs during stomatal movement. Transcription factors (TFs) such as AREB/ABFs up-regulate the expression of ADF5, which stabilizes actin filaments to promote stomatal closure. Additional ADFs (ADF1/2/3/4/6) may also be involved in ABA-regulated stomatal closure via TR.