Figure 4. Aberrant splicing of TIP60 affects its activity and DNA repair pathway choice.
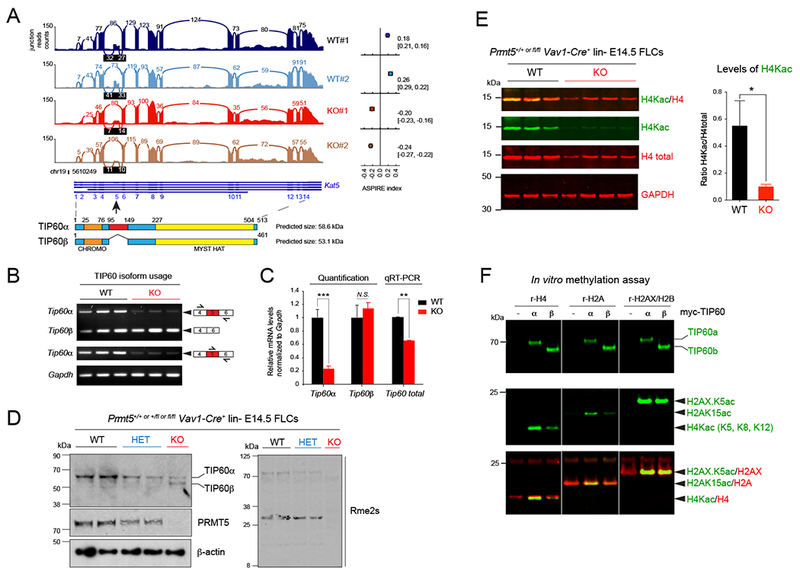
(A) Sashimi plot showing the decreased read counts between exons 4 and 5 and between exons 5 and 6 of the gene Kat5 coding for the protein TIP60. The ASPIRE index on the right indicates a decreased usage of exon 5 in PRMT5 KO Ter119− FLCs compared to WT cells and was calculated with AltAnalyze. Below the Sashimi plot, the structures of Kat5 and of TIP60 are shown.
(B) Semi-quantitative PCR of the indicated transcripts in E14.5 Ter119− PRMT5WT vs KO FLCs.
(C) Quantification of the relative abundance of Kat5/Tip60 isoforms shown in (B) and total mRNA in E14.5 Ter119− PRMT5 WT vs KO FLCs by real-time PCR using a Taqman probe that recognizes both TIP60 isoforms, relative to Gapdh. Error bars are SEM of at least 3 biological replicates. *** P<0.0001, ** P<0.01, N.S. non-significant.
(D) Immunoblot showing aberrant splicing of TIP60 in E14.5 lin− PRMT5 +/+ (WT), +/Δ (HET), and Δ/Δ (KO) FLCs, and decreasing levels of arginine methylation after PRMT5 loss.
(E) Multiplex immunoblots showing decreased H4 acetylation in PRMT5 KO E14.5 Ter119− FLCs. Quantification of H4Kac relative to H4 (n=5 biological replicates) is shown on the right. Error bars are SEM. * P<0.05.
(F) In vitro acetylation experiment and multiplex immunoblots with TIP60, H2AXK5ac, H2AK15ac, H4K5/8/12ac, and total H2A & H4 antibodies. Myc-tagged TIP60 proteins (full length or α vs shorter isoform or β) were immunoprecipitated from transiently transfected 293T cells, and incubated with recombinant histones H4, H2A or the H2AX/H2B dimer.
