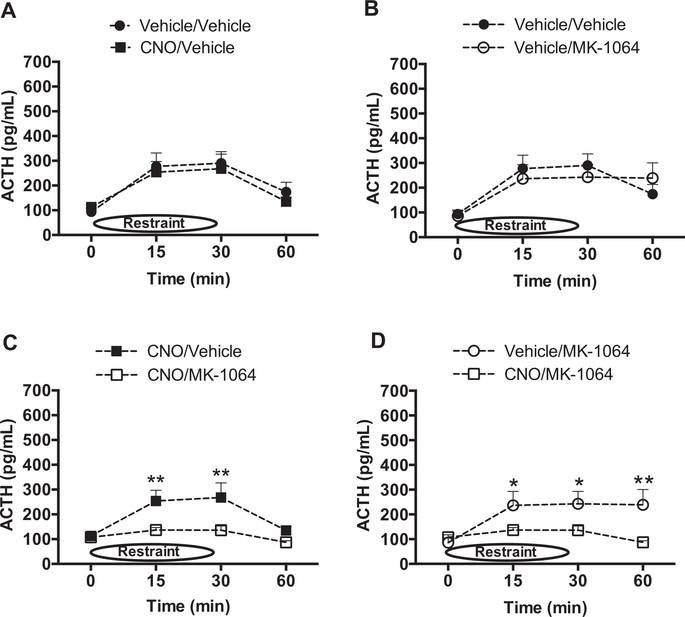
Fig. 5.
OX2R- and non-OX2R-mediated orexin mechanisms have opposing influences on ACTH responses to repeated restraint stress. (n = 12/group) ACTH levels were evaluated on the fifth day of restraint stress following vehicle/vehicle versus CNO/vehicle pretreatment to evaluate orexin neuron activation (A; no significance by ANOVA), vehicle/vehicle versus vehicle/MK-1064 pretreatment to evaluate the role of endogenous OX2R (B; no significance by ANOVA), CNO/MK1064 versus CNO/vehicle pretreatment to assess the effect of exogenous OX2R activity induction (C; significant: 2-Way ANOVA, Drug: F(1,45) = 13.1, p = 0.001), or Vehicle/MK-1064 versus CNO/MK-1064 pretreatment to understand the role of orexin-induced mechanisms other than OX2R (D; significant: 2-Way ANOVA, Drug: F(1,40) = 12.02, p < 0.01). *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01.