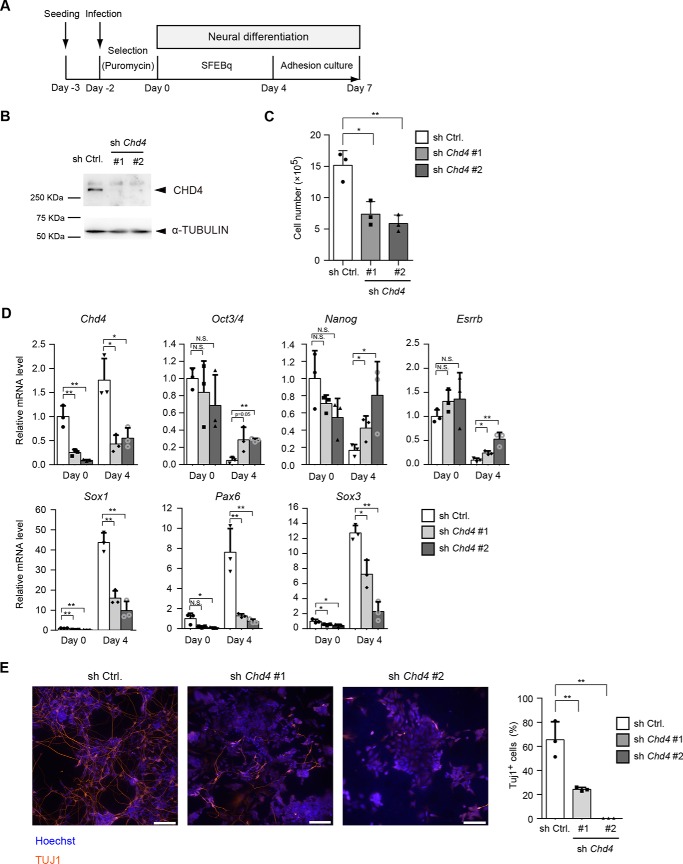
Figure 1.
CHD4 is required for neural differentiation of ESCs. A, scheme for shRNA-mediated Chd4 knockdown and subsequent neural differentiation. ESCs were infected with a lentivirus encoding Chd4 shRNAs (sh Chd4 #1 or #2) or control shRNA (sh Ctrl.) and were cultured under selection with puromycin for 2 days. The SFEBq culture method was used for neural differentiation. SFEBq-cultured cells at day 4 were then subjected to adhesion culture for further neural differentiation. B, immunoblotting analysis for CHD4 and α-tubulin (as a loading control) in control shRNA- and Chd4 shRNA-expressing cells at day 0. C, effect of Chd4 shRNAs on the number of ESCs. One day before viral infection (day −3), 2.5 × 105 cells were plated, and cells were counted at day 0. D, qRT-PCR analysis of Chd4, pluripotency genes (Oct3/4, Nanog, and Esrrb), and neural genes (Sox1, Pax6, and Sox3) in control shRNA- and Chd4 shRNA-expressing cells at day 0 and day 4. Each mRNA level was normalized to the β-actin level, and the value of control shRNA-expressing cells at day 0 was set to 1. E, cells at day 7 were stained for TUJ1 (left). The scale bars represent 100 μm. The percentages of TUJ1-positive cells are shown (right). C–E, data are shown as the means ± S.D. (n = 3 independent experiments). *, p < 0.05, and **, p < 0.01. N.S., not significant. The p values were calculated using Student's unpaired two-tailed t tests compared with the control cells in the same day.