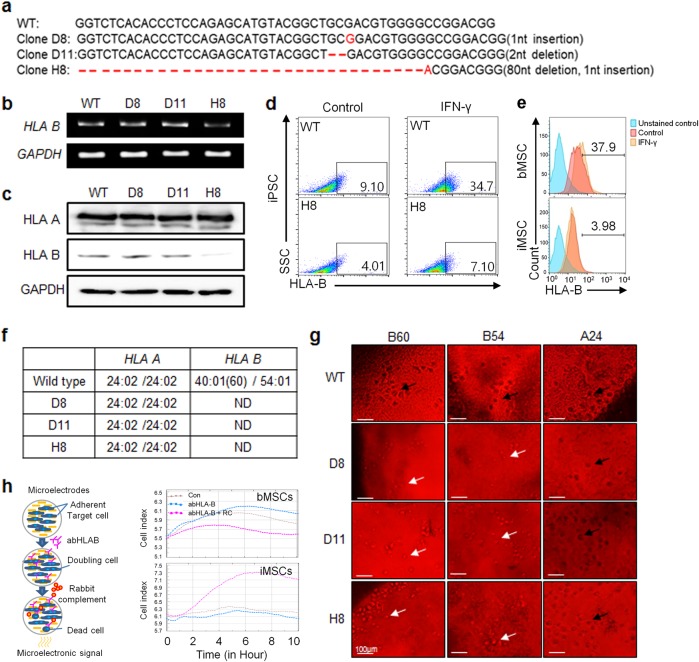
Fig. 2. HLA-B sequence and immunogenicity analysis of CRISPR-engineered inducible pluripotent stem cells.
a Nucleotide sequence analysis of HLA-B–engineered iPSC clones. Expression analysis of HLA-B in HLA-B-engineered iPSC clones at the b mRNA and c protein levels. The flow cytometric analysis of HLA-B-expression in d wild-type and HLA-B-engineered iPSCs and e HLA-B-engineered iPSC-derived MSCs. The cells were unstimulated or stimulated with IFN-γ for the induction of HLA-B overexpression. bMSCs were used as the control. f HLA-typing analysis of HLA-B-engineered iPSC clones. HLA typing was performed with sequence-based typing (SBT). (ND; not determined). g Complement-dependent cytotoxicity analysis of HLA-B-engineered iPSC clones. To analyze complement-dependent cytotoxicity, serological HLA-B typing was performed using Terasaki HLA Tissue Typing Trays. For complement-dependent cytotoxicity, the cells were incubated with HLA–A (*24) or –B (*54 or *60) specific antiserum. Living and dead cells were determined by eosin staining. Black arrows represent dead cells. White arrows indicate live cells. h X-celligence scheme (left panel). Antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity (ADCC) of HLA-B-engineered iPSC-derived MSCs using x-celligence (right panel). bMSCs were used as the control