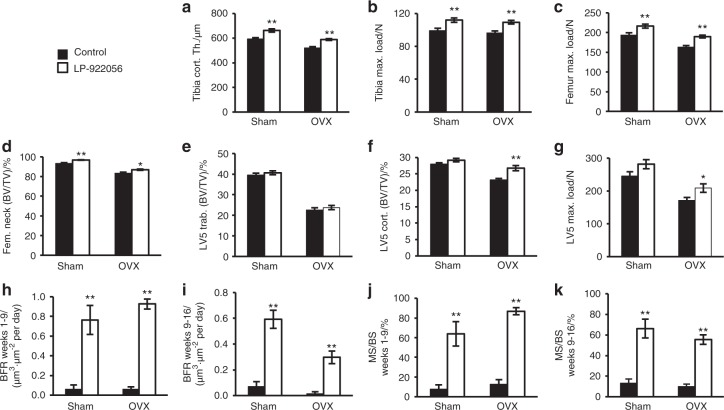
Fig. 5.
Treatment with orally active small molecule NOTUM inhibitor increases cortical bone thickness and strength in ovariectomized rats. Female rats were ovariectomized (OVX) or sham operated at 21 weeks of age and 18 weeks of treatment with NOTUM inhibitor LP-922056 (daily oral gavage; 30 mg·kg−1 per day), or vehicle control was initiated 37 weeks later (N = 12–13). a Time course of total femur BMD analyzed by DXA throughout the study (P < 0.05 for LP-922056 vs control for both gonadal intact and OVX rats at 6, 12, and 18 weeks of treatment), b Distal tibia cortical thickness. c, d Midshaft bone strength in tibia (c) and femur (d) (maximum load; Max. load) as measured by 3-point bending. e Femur neck bone volume per total volume (BV/TV; mainly reflecting cortical bone). f Vertebral trabecular bone volume per total volume (BV/TV; central part of vertebral body; L5). g Vertebral body cortical shell bone volume per total volume (BV/TV; reflecting cortical bone, L5). h Vertebral compression bone strength (maximum load; Max. Load; LV5). i–l Dynamic histomorphometry of distal tibia cortical bone (N = 6). Rats were injected with alizarin, demeclocycline and calcein at weeks 1, 9, and 16, respectively. Endocortical BFR during weeks 1 to 9 (i) and weeks 9 to 16 (j) and corresponding endocortical MS values (k and l) are shown. Values are means ± SEM. *P < 0.05 and **P < 0.01 vs control