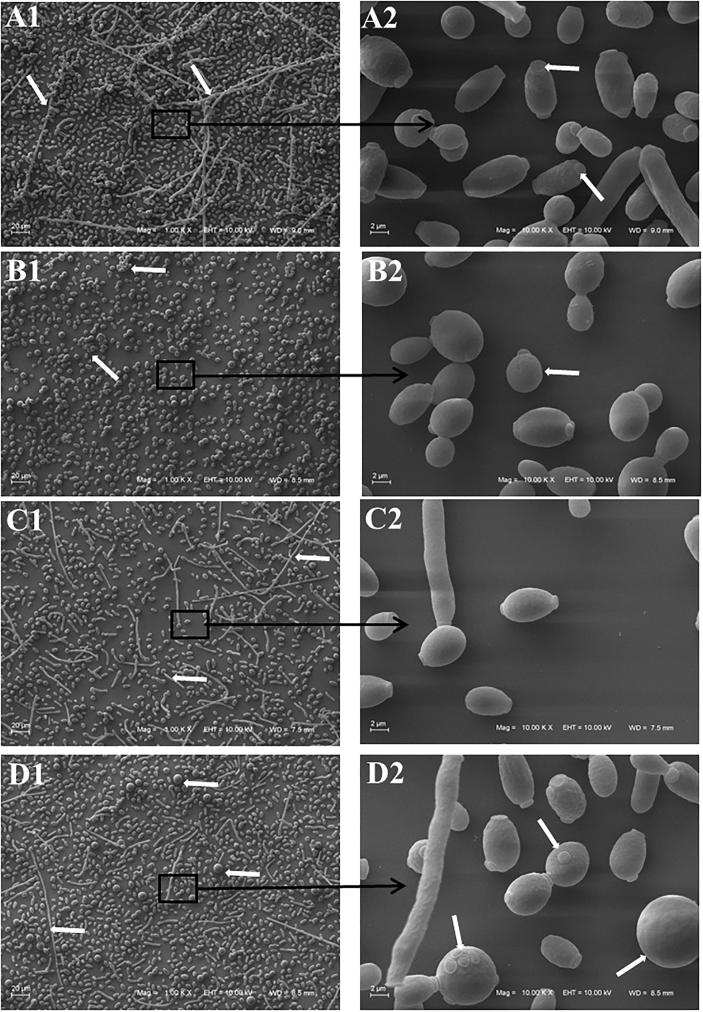
Fig. 3.
Scanning electron microscopy of Candida albicans ATCC 18804 treated with sub-inhibitory concentration of 8-hydroxyquinoline derivatives 1–3 (1: clioquinol; 2: 8-hydroxy-5-quinolinesulfonic acid; 3: 8-hydroxy-7-iodo-5-quinolinesulfonic acid) and untreated cells. A. Untreated cells; A1 (Bar = 20 µm): white arrows indicate pseudohyphae; A2 (Bar = 2 µm): white arrows indicate polar bud scars. B. Hyphal cells treated with clioquinol 1; B1 (Bar = 20 µm): white arrows indicate cell clusters; B2 (Bar = 2 µm): white arrow indicates rounded cells. C. Hyphal cells treated with derivative 2; C1 (Bar = 20 µm): white arrows indicate pseudohyphae with few blastoconidia and chlamydospore; C2 (Bar = 2 µm). D. Hyphal cells treated with derivative 3; D1 (Bar = 20 µm): white arrows indicate pseudohyphae with few blastoconidia and larger round cells; D2 (Bar = 2 µm): white arrows indicate pseudohyphae with few blastoconidia and larger round cells.