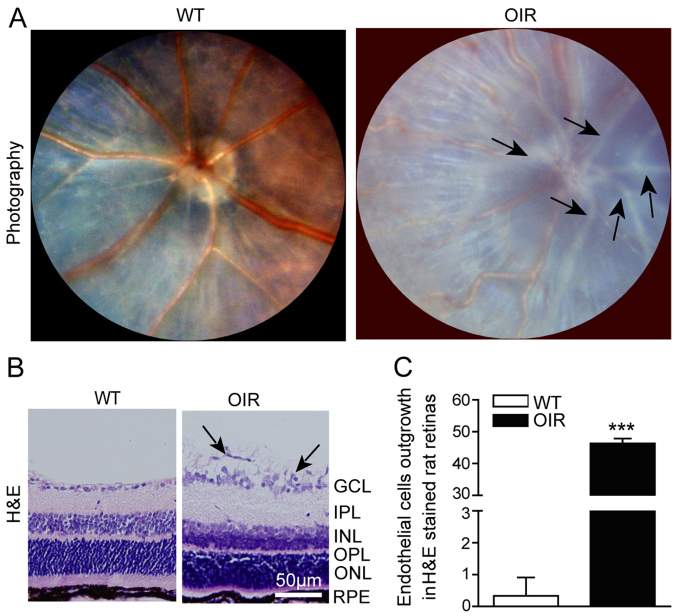
Figure 1.
RNV is generated in OIR mice. (A) Fundus photography facilitated visualization of the inner surfaces of the eyes of the WT and OIR mice. The representative images indicate the large number of pale neovascular vessels that had grown into the vitreous cavity in the OIR mice, compared with the WT mice. (B) Representative H&E staining of retinal sections. A large number of the neovascular nuclei were present beyond the internal limiting membrane in the OIR mice, while there were only a few neovascular nuclei in the WT mice. (C) The number of outgrowth endothelial cells in the retinas was calculated using Image-Pro Plus software. The number of neovascular nuclei in the OIR mice was significantly greater compared with that of the control mice. Data are presented as the mean ± standard deviation of the mean (n=6 mice per group). ***P<0.001 vs. WT mice. GCL, ganglion cell layer; IPL, inner plexiform layer; INL, inner nuclear layer; OPL, outer plexiform layer; ONL, outer nuclear layer; RPE, retinal pigment epithelium. H&E, hematoxylin and eosin; OIR, oxygen-induced retinopathy; WT, wild-type.