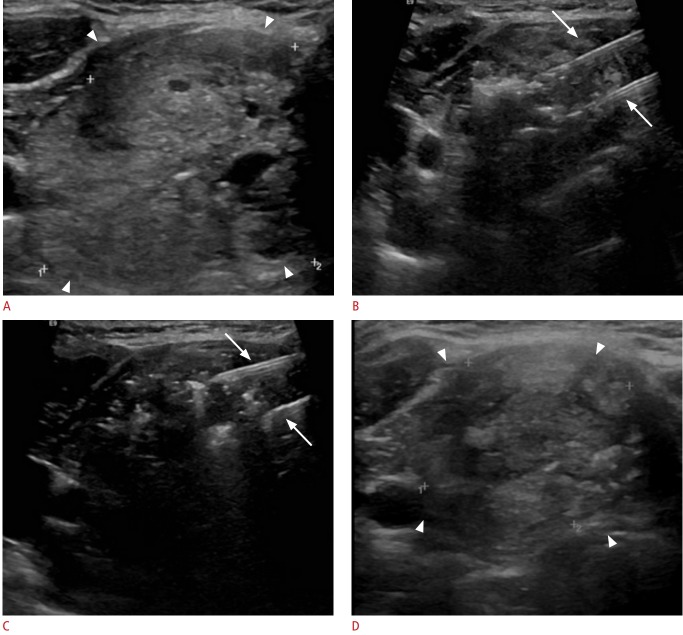
Fig. 2. Ultrasonography of a 62-year-old patient with a benign thyroid nodule treated with laser ablation.
A. Ultrasonography shows a large, isoechoic, non-homogeneous, predominantly solid thyroid nodule (arrowheads). B. Ultrasonography during treatment shows two parallel laser fibers that are clearly visible as hyperechoic lines (arrows), and hyperechoic areas due to gas formation during ablation around the tip of the laser fibers. C. Ultrasonography after one pull-back of the two laser (arrows) fibers shows the two laser fibers visible as hyperechoic lines, while an area of non-homogeneous hyperechogenicity is seen in the previously ablated area, corresponding to residual gas after treatment. D. Ultrasonography taken 2 months after treatment demonstrates a 58% volumetric reduction of the treated nodules, which appear as isoechoic and non-homogeneous (arrowheads).