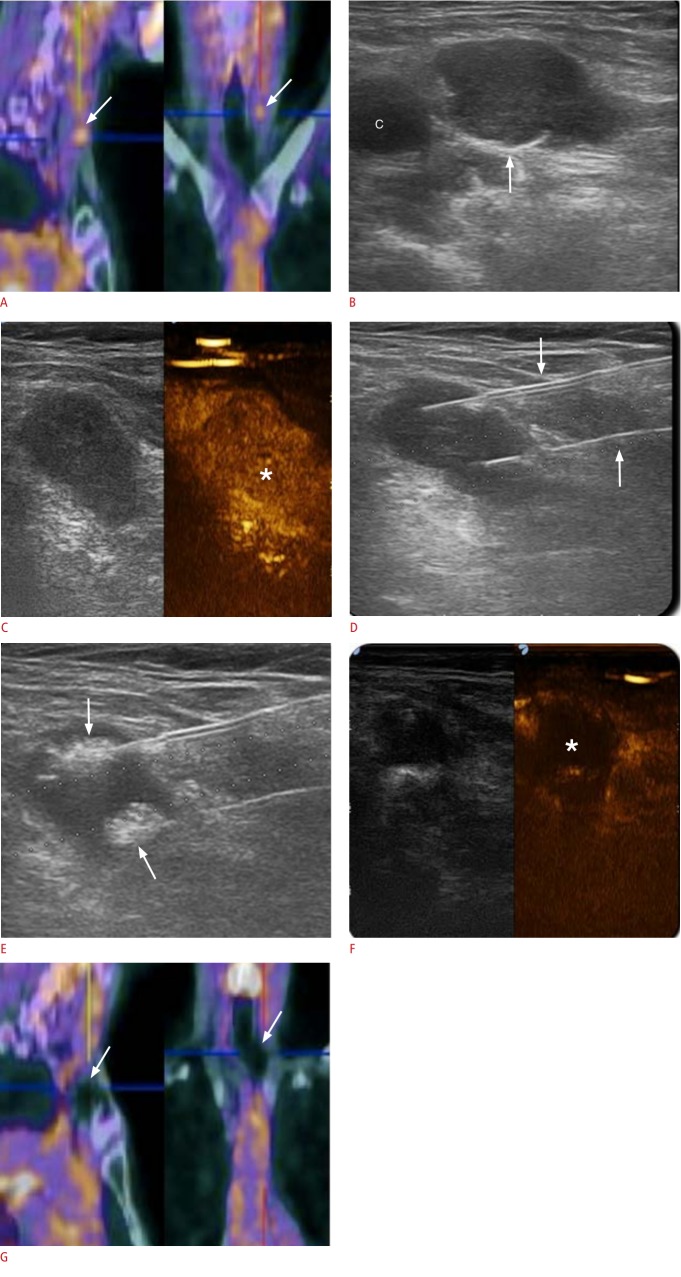
Fig. 3. 18-Fludeoxyglucose positron emission tomography (18FDG-PET) and ultrasonography in a 73-year-old patient with previous papillary thyroid carcinoma and a cytologically proven metastatic lymph node treated with laser ablation.
A. 18FDG-PET scan shows a left cervical area of focal intense uptake (arrows) representing a metastatic lymph node. B. Ultrasonography performed at the same level shows a hypoechoic oval-shaped lymph node, with loss of normal nodal appearance (arrow; c, carotid artery). C. Contrast-enhanced ultrasonography demonstrates intense enhancement of the lymph node (asterisk). D. Ultrasonography during the treatment shows two laser fibers, visible as hyperechoic lines (arrows), extending into the lymph node. E. Ultrasonography during ablation shows two hyperechoic areas around the tip of the two laser fibers (arrows), reflecting gas formation during ablation. F. Post-treatment contrast-enhanced ultrasonography demonstrates the lack of enhancement in the treated lymph node (asterisk). G. 18FDG-PET after treatment shows no uptake at the level of the previously treated lymph node (arrows).