Figure 5. Alcohol-odor training causes lasting changes to Notch in MB neurons.
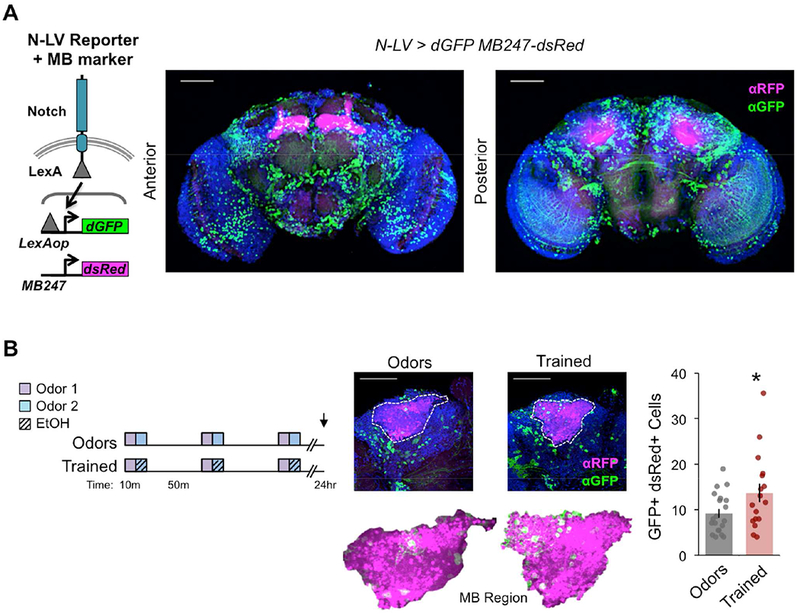
(A) Schematic of Notch-LexA:VP16 (N-LV) reporter driving destabilized GFP LexAop-dGFP and MB247-dsRed MB marker. GFP signal, a proxy of Notch activity, was extensive and broadly observed in the anterior and posterior central brain. (B) Trained N-LV>dGFP MB247-dsRed (all transgenes heterozygous) flies showed more GFP+ dsRed+ cells as compared to Odors only treatment 24 hours after training; n = 20, 17 flies (averaged across left and right hemispheres scored from confocal series). Mean ± SEM with statistical significance evaluated by two-tailed T- test, *p < 0.05. (A-B) Images are max projection stacks with Dapi (blue), dGFP (green), and dsRed (magenta); scale bar 50 μm. See also Figure S6.
