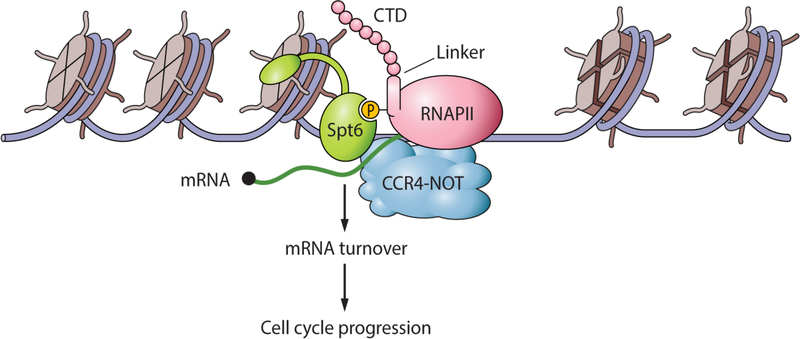
Figure 7. Model showing the connections between Spt6 and the regulation of mRNA turnover.
The model summarizes our finding that Spt6-RNAPII association is key to the recruitment and activity of the Ccr4-Not complex that regulates mRNA turnover. Uncoupling of Spt6 and RNAPII produces increased amounts of cell cycle-associated mRNAs (due to lack of turnover of a broad range of mRNAs) that cause cell cycle defects. Our model depicts Spt6 associating with a newly described phosphorylated linker region in RNAPII that has been found to bind Spt6; however, the Spt6 chaperone also interacts with phosphorylated residues in the RNAPII C-terminal domain (CTD) (not shown; see text for details). These results uncover a previously unknown function for the Spt6 histone chaperone in transcriptional regulation.