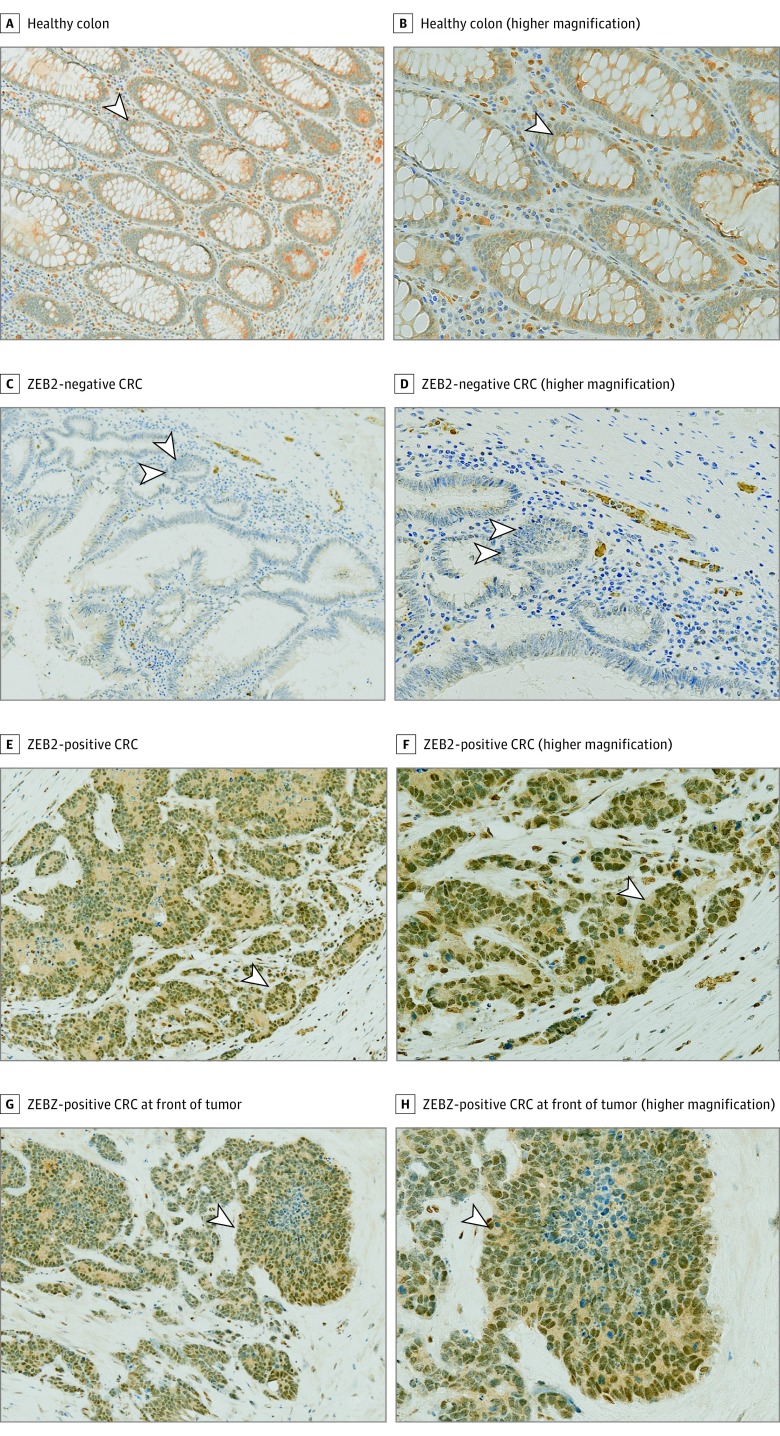
Figure 1. Immunohistochemical Analysis of ZEB2 Expression in Healthy Colon and Colorectal Cancer (CRC) Specimens.
A and B, Healthy colonic epithelium. The arrowheads indicate cells with an absence of ZEB2 nuclear staining (A) and fibroblasts and immune cells with positive nuclear staining that served as internal positive controls (B). C and D, Representative example of a CRC specimen that stained negative for ZEB2. Arrowheads indicate cells with an absence of ZEB2 nuclear staining (C) and fibroblasts and immune cells that served as internal positive controls (D). E and F, Representative example of a CRC specimen that stained positive for ZEB2. Arrowheads indicate CRC specimen expressing nuclear ZEB2 in neoplastic cells (E) and staining of cells in the middle of the cluster of neoplastic cells and evidence of the specificity of the antibody (F). G and H, A CRC specimen that was ZEB2 positive at the invasive front of the tumor. Immunohistochemical analysis for ZEB2 (brown) was performed on all images, visualized by 3,3′-diaminobenzidine–positive chromogen, and counterstained with hematoxylin (blue) (original magnification ×100 [A, C, E, and G] and ×200 [B, D, F, and H]). Arrowheads indicate nuclear positivity.