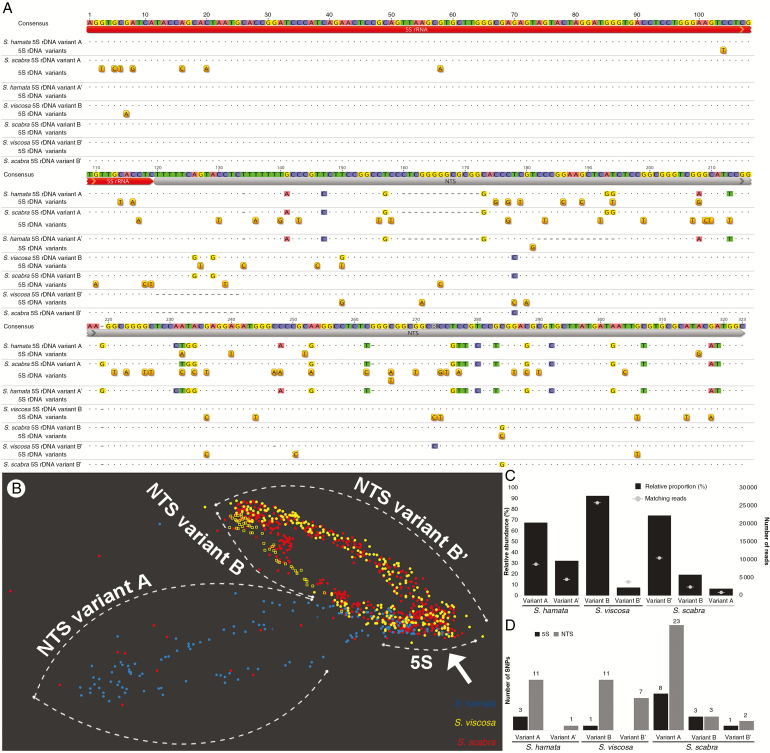
Fig. 4.
5S rDNA sequence characterization in Stylosanthes. (A) Alignment of 5S (red) rDNA variants including the NTS region (grey) of S. hamata, S. viscosa and S. scabra. Positions of SNPs detected are drawn under each respective sequence. (B) SeqGrapheR visualization of RepeatExplorer 5S rDNA cluster including reads of all three species. Note the close grouping of S. scabra and S. viscosa reads along the NTS region, while the coding 5S region groups reads from the three species (arrow). A few reads (red dots) from S. scabra are seen along NTS variant A, which is in agreement with the low abundance of this variant in the allopolyploid genome. (C) Relative abundance and number of reads matching each 5S rDNA variant found in Stylosanthes. (D) Number of SNPs found in each variant sorted by the 5S coding and NTS regions. Note the high level of SNPs found in variant A of S. scabra.