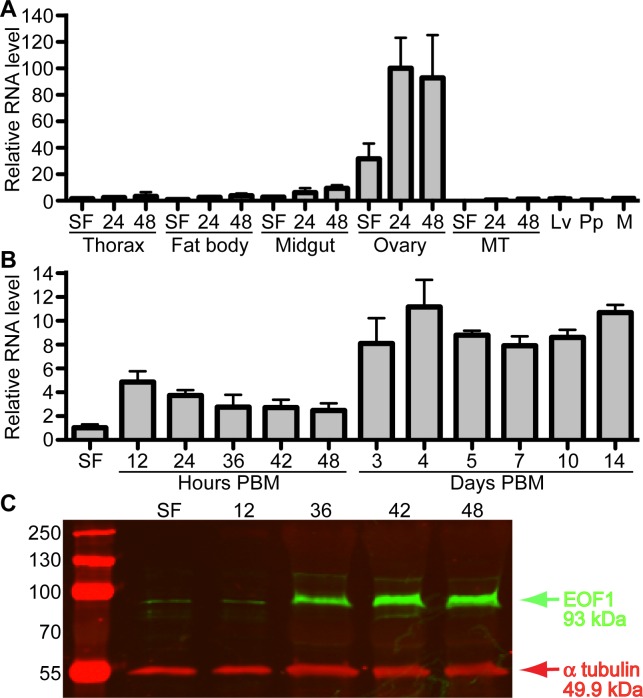
Fig 3. Spatial distribution and expression level of EOF1 during the first gonotrophic cycle in A. aegypti.
(A) Tissue-specific and developmental expression pattern of EOF1 during the first gonotrophic cycle of A. aegypti mosquitoes was determined. EOF1 gene expression was analyzed by qPCR using cDNAs prepared from various tissues. Tissues include thorax, fat body, midgut, ovary, and MTs in SF only and 24 and 48 h PBM, as well as Lv, Pp, and M. The pattern demonstrates the ovary-specific EOF1 expression in A. aegypti mosquitoes. The EOF1 expression levels were normalized to S7 ribosomal protein transcript levels in the same cDNA samples. Data were collected from three different mosquito cohorts. EOF1 expression in fat body at SF was set to 1.0. (B) Detailed EOF1 gene expression in ovaries and follicles were analyzed by qPCR using cDNAs from mosquito ovaries or follicles. Samples from SF to 42 h PBM include entire ovaries, whereas those from 48 h to 14 days PBM include only follicles (primary and secondary follicle cells and germarium) isolated from ovaries to exclude nonfollicle cells in the oviducts and ovarioles. EOF1 expression in ovaries at SF was set to 1.0. (C) EOF1 protein expression pattern in ovaries were determined by western blot analysis using an EOF1-specific polyclonal antibody. Each lane contains 0.3 ovary equivalent of protein extracts. α-tubulin was used as an internal control. qPCR and western blot experiments were performed in triplicate. Underlying data can be found in S1 Data. cDNA, complementary DNA; EOF1, eggshell organizing factor 1; Lv, larvae; M, adult male; MT, Malphigian tubule; PBM, post-blood meal; Pp, pupae; qPCR, quantitative real-time PCR; SF, sugar fed.