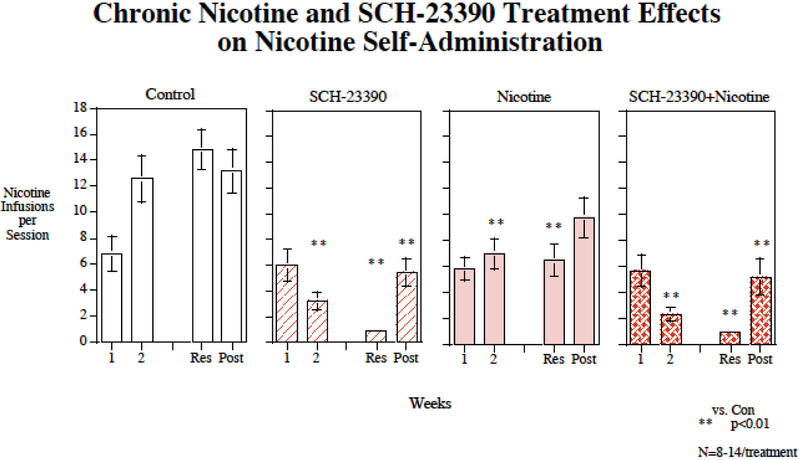
Figure 1:
Repeated SCH-23390 injections interacting with chronic nicotine infusion, affect IV nicotine self-administration The weeks listed are weeks of drug treatment with four weeks of chronic nicotine infusion (Week 1 through resumption) and three weeks of lorcaserin injections (Week 2 through nicotine access resumption). Average infusions per session refer to the average number of nicotine infusions delivered per 60-min self-administration session with each treatment condition. Results from nicotine self-administration sessions, averaged over week-long periods of the experiment (weeks 1 and 2 of continued nicotine access (1 and 2), resumed access (Res) and post-treatment (Post), grouped by treatment condition. Chronic continuous nicotine infusions (4 weeks at 2.5 mg/kg/day) and chronic s.c. SCH-23390 (4 weeks at 0, or 0.02 mg/kg) injection effects on IV nicotine self-administration, weekly average response for the entirety of the experiment. Data represent mean ± sem, N=9-14/treatment