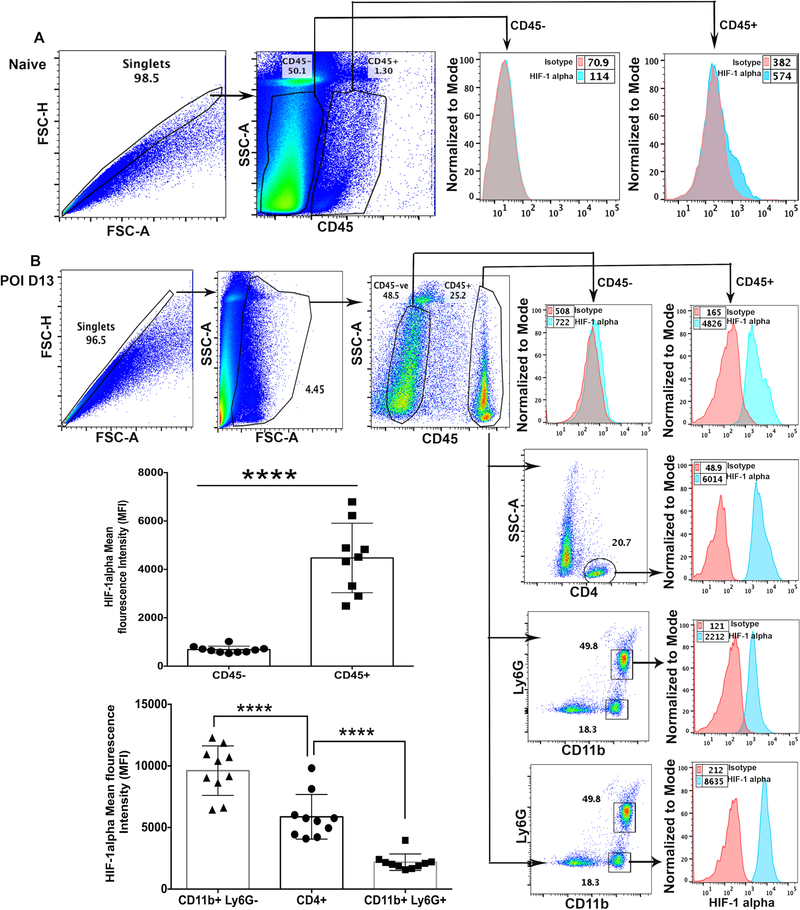
Figure 6.
Hypoxia inducible factor-1α (HIF-1α) protein accumulation in immune cell subsets in HSK developing corneas. (A) Representative pseudocolor FACS plot of five pooled naive corneas denote the gating strategy employed for CD45- non-leukocytes and CD45+ leukocytes. Representative histogram FACS plot (right) shows isotype control and the level of intracellular HIF-1α protein in CD45- and CD45+ cell populations, respectively. Data shown is derived from two independent experiments. (B) Representative FACS plots showing HSV-1 infected corneas at 13-day POI demonstrate gating strategy employed for CD45- non-leukocytes, CD45+ leukocytes, CD4 T cells, CD11b+Ly6G+ neutrophils, and CD11b+Ly6G- non-granulocytic myeloid cells. Representative histogram FACS plots (from top to bottom) show isotype control and an intracellular level of HIF-1α protein in non-leukocytes, leukocytes, CD4 T cells, neutrophils, and myeloid cells in infected cornea. Scatter plot/bar graph demonstrates the MFI of HIF-1α protein in non-leukocytes vs leukocytes and in three different leukocyte cell subsets in individual infected corneas at 13-day POI. Data shown is derived from two similar experiments with n= 5 mice /group in each experiment. Statistical significance was calculated using unpaired non-parametric t-test and one-way ANOVA test. **** p<0.0001.