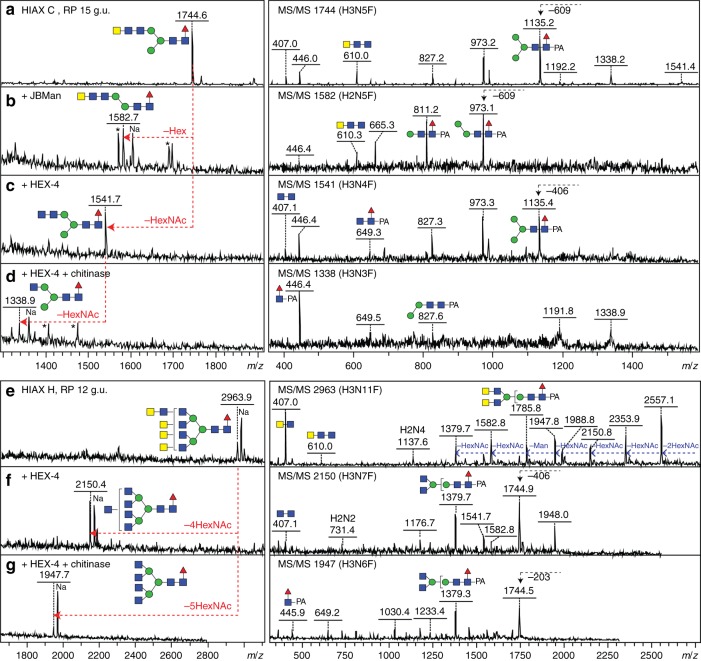
Fig. 2.
Example glycosidase digestions of N-glycans with tri- and di-HexNAc motifs. Pyridylaminated Hex3HexNAc5Fuc1 (m/z 1744) and Hex3HexNAc11Fuc1 (m/z 2963) glycans isolated in different 2D-HPLC fractions (Fig. 1, HIAX C and H) were subject to positive mode MALDI-TOF–MS (left) and MS/MS (right) before (a, e) and after treatment with either jack bean α-mannosidase (b), C. elegans HEX-4 (c, f) or C. elegans HEX-4 followed by Streptomyces chitinase (d, g). Contaminant peaks in enzyme digests (B and D; m/z 1570, 1689, 1696, 1407 and 1476) are indicated by asterisks. The MS/MS spectra are annotated with selected B- and Y-ion fragments (the latter, e.g. m/z 446, 973 or 1176, containing the reducing terminal PA label with the possible structure for the selected fragments based on the assumption of a single fragmentation event) as well as relevant serial losses (indicated in blue) or a single loss of 203, 406 or 609 from the parent (i.e. HexNAc1-3; indicated with black arrows); the loss of m/z 407 or 610 B-ions (HexNAc2-3) upon HEX-4 or chitinase digestions are indicative of removal of antennal GalNAc or GlcNAc residues. As defined by this and other data (including Supplementary Figures 6, 8 and 23, previous publications as well as controls with LacdiNAc and chitobiose-glycoconjugates and standard N-glycans), C. elegans HEX-4 is specific for β1,4-linked GalNAc and chitinase for either β1,4-linked HexNAc. Thereby, the nature of the HexNAc2 and HexNAc3 motifs of the m/z 1744 and 2963 glycans can be defined