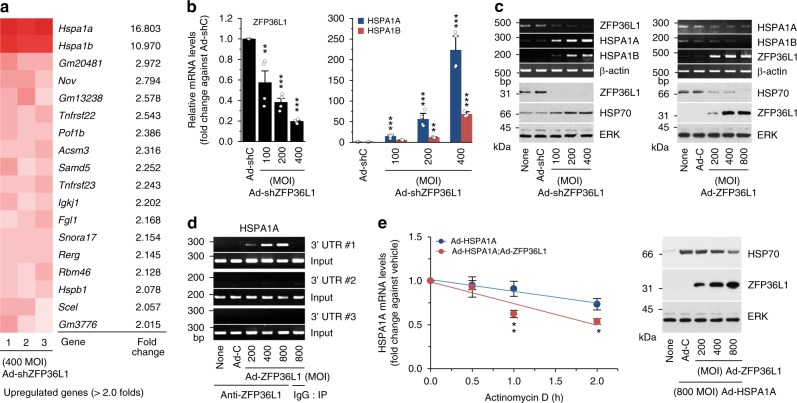
Fig. 4.
ZFP36L1 targets HSP70 family members in chondrocytes. a Microarray analysis of chondrocytes infected with 400 MOI of Ad-shZFP36L1 to knock down ZFP36L1 (3 replicates). b, c qRT-PCR (b) and RT-PCR and western blot analyses (c) of ZFP36L1, HSPA1A, HSPA1B, and HSP70 in chondrocytes infected with Ad-C (800 MOI) or the indicated MOIs of Ad-shZFP36L1 or Ad-ZFP36L1 for 36 h (n = 4). Representative images are presented (c). d RNA binding of ZFP36L1 in chondrocytes infected with Ad-C or Ad-ZFP36L1. The binding of ZFP36L1 to the 3′-UTR of HSPA1A was determined by RT-PCR of immunoprecipitates obtained using anti-ZFP36L1 or IgG. Representative images are presented from five biologically independent samples. e mRNA decay assay. Chondrocytes were infected with Ad-HSPA1A with or without Ad- ZFP36L1 for 12 h, and then exposed to Actinomycin D (1 μg ml−1) for the indicated time periods. The mRNA levels of HSPA1A were quantified by qRT-PCR analysis (n = 9). Representative western blot images of HSP70 and ZFP36L1 proteins. Means ± s.e.m. with one-way ANOVA (*P < 0.01, **P < 0.001, and ***P < 0.0001)