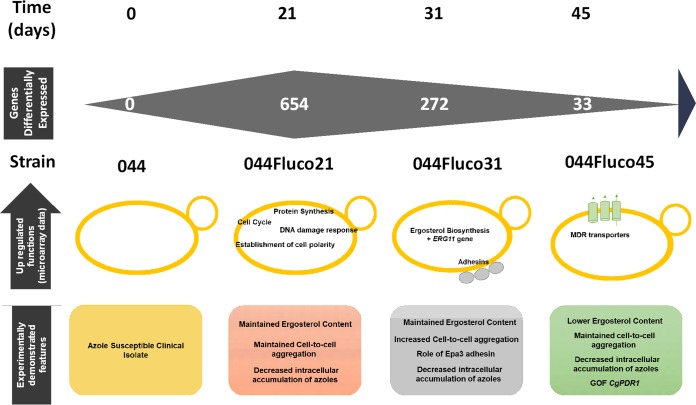
FIG 12.
Current model for the mechanisms underlying the evolution of the 044 clinical isolate toward multiazole resistance. Under the timeline of prolonged fluconazole exposure, indicating the days at which resistance to each azole drug was achieved, the main biological processes found to be upregulated in each of the azole-resistant strains are highlighted. Below, the conclusions of the experimental results obtained are given, suggesting that while for 044Fluco21, drug resistance appears to rely mostly on decreased drug accumulation due to increased CgCdr1 expression, the 044Fluco31 strain displays increased drug tolerance due to increased cell-to-cell adhesion, and 044Fluco45 exhibits multiazole resistance due to the acquisition of a CgPdr1 GOF mutation leading to increased expression of CgCdr1 and CgCdr2.