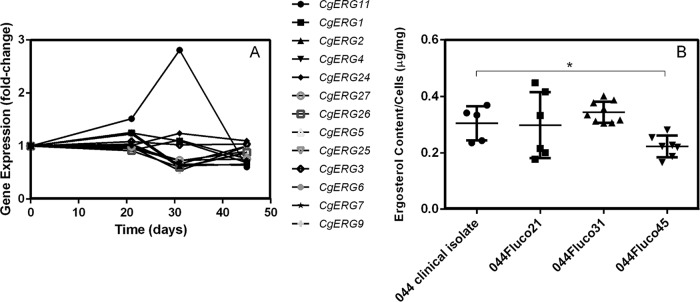
FIG 3.
Role of ergosterol metabolism in the acquisition of azole resistance in the 044 clinical isolate. (A) Gene expression changes registered for ergosterol biosynthetic genes along the evolution of the 044 clinical isolate toward multiazole resistance. Transcript levels were obtained by microarray hybridization, and for each, the fold change relative to the level registered for the 044 parental clinical isolate is shown. Values are averages of results from at least three independent experiments. P < 0.05. (B) Total ergosterol contents of 044 and azole-derived C. glabrata cells. Cells were harvested after 15 h of growth in YPD medium, and total ergosterol was extracted and quantified by HPLC. Cholesterol was used as an internal standard in order to evaluate the yield of the ergosterol extraction. The ergosterol contents displayed are averages of the results of at least three independent experiments. Error bars represent standard deviations. *, P < 0.05.