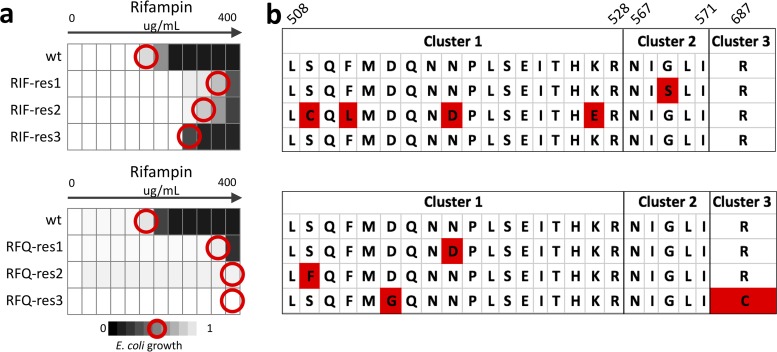
FIG 2.
E. coli exposed to rifampin or the drug degradation product rifampin quinone show similar patterns of rifampin resistance and genetic changes. E. coli resistant to either RIF (RIF-res, a) or the drug degradation product RFQ (RFQ-res; b) over 5 days were assessed for stable increase in RIF MIC compared with solvent-treated controls (wild type [WT]). RFQ-res populations showed cross-resistance to rifampin, with up to a 64-fold increase in IC50 (red circles). Each population was assessed for genetic changes in the RRDR of the rpoB gene (c). The majority of populations that acquired resistance to either RIF or RFQ acquired nonsynonymous mutations in the RRDR clusters of the rpoB gene. These mutations are consistent with previous reports of rifampin resistance due to rpoB mutations.