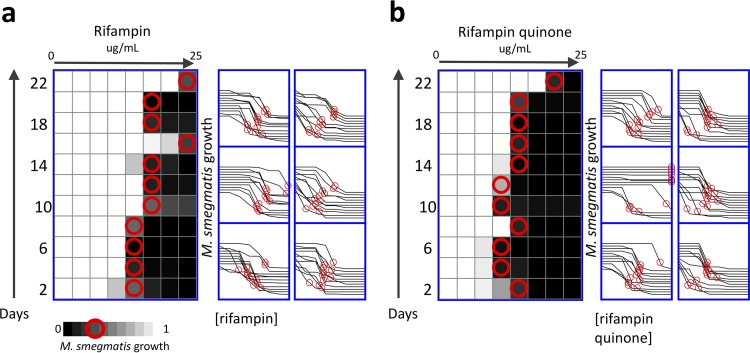
FIG 3.
Selection of resistance in Mycobacterium smegmatis exposed to rifampin and the drug degradation product rifampin quinone. M. smegmatis bacteria were cultured in a range of concentrations of either rifampin (a) or the drug degradation product rifampin quinone (b), with 2-fold increments of concentrations (n = 6). These selections represent independent experiments conducted in parallel. Every 48 h, bacteria were selected from the concentration at approximately IC75 (red circles), diluted in fresh media, and aliquoted to a fresh range of drugs. All experiments were conducted with 6 biological replicates, with each heatmap corresponding to the upper left dose-response curves. The right shift in dose-response curves over time demonstrates that M. smegmatis acquired up to a 10-fold increase in IC75 after exposure to rifampin (a) and a 13-fold increase in IC75 after exposure to rifampin quinone (b).