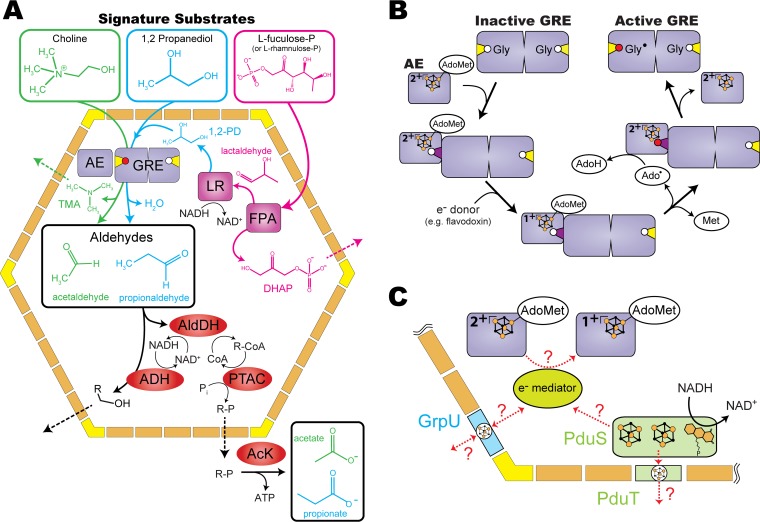
FIG 1.
Overviews of GRM functional diversity and GRE activation. (A) Catabolic pathways for the three different substrates processed by distinct GREs encapsulated in GRMs: choline (green), 1,2-propanediol (1,2-PD) (cyan), and l-fuculose-P (or l-rhamnulose-P) (magenta and cyan). (B) GRE activation requires an activating enzyme (AE) and an external source of electrons. The active site glycine residue (white circle) located on the glycyl radical loop (closed conformation in yellow and open conformation in dark purple) is converted to a glycyl radical (Gly· [red circle]) after hydrogen abstraction by the adenosyl radical (Ado·). Iron-sulfur (FeS) clusters are represented by orange (Fe) and black (sulfur) spheres. (C) Hypothetical redox reactions and electron transfer pathways involving PduS/PduT and/or GrpU. Abbreviations: ADH, alcohol dehydrogenase; AldDH, aldehyde dehydrogenase; PTAC, phosphotransacylase; AcK, acetate kinase; LR, lactaldehyde reductase; FPA, fuculose-P aldolase; DHAP, dihydroxyacetone phosphate. See the text for details.