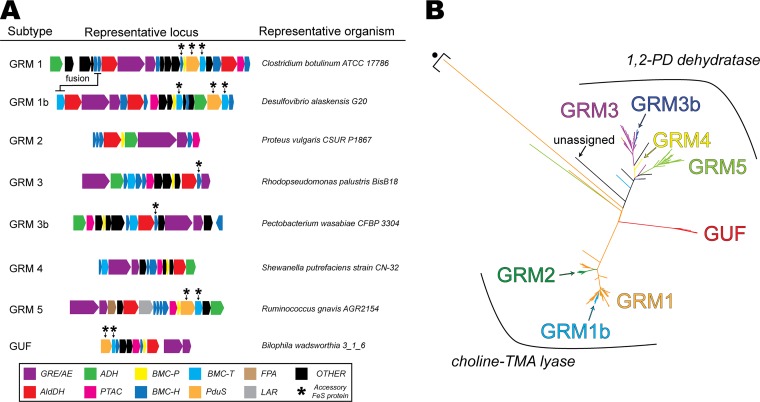
FIG 2.
GRM locus variability, distribution of accessory FeS proteins, and GRE phylogeny. (A) Diagrams of loci for representative organisms encoding each GRM subtype. The accessory FeS proteins PduS, PduT, and GrpU are marked with black asterisks. (B) Phylogenetic tree of GRM GRE amino acid sequences showing they cluster predominantly by both subtype (GRM1, orange; GRM1b, light blue; GRM2, dark green; GRM3, purple; GRM3b, dark blue; GRM4, yellow; GRM5, light green; GUF, red; unassigned, black) and function (GRM1, -1b, and -2 genes encode choline-trimethylamine lyases; GRM3, -3b, -4, and -5 genes encode 1,2-PD dehydratases). Examples of GRM1 and GRM5 GREs that do not cluster with other sequences from their respective subtypes are marked by a black dot and square bracket.