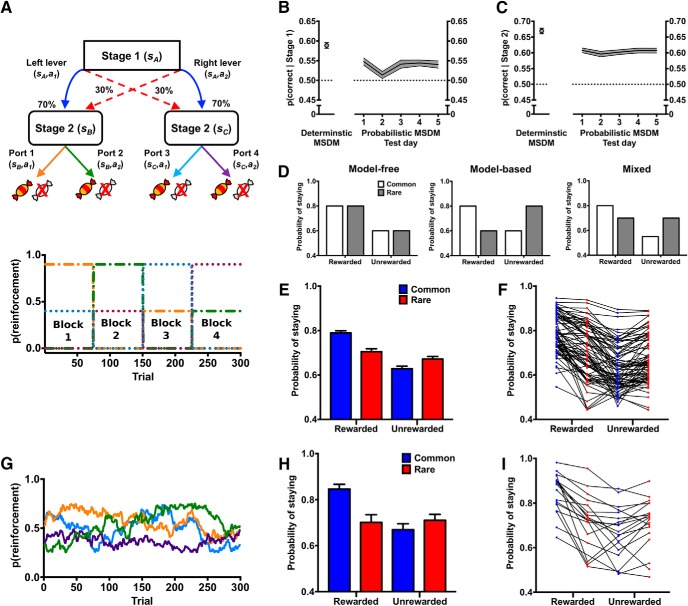
Figure 2.
Decision-making in the probabilistic MSDM. A, Rats were assessed on the probabilistic MSDM task, which was similar in structure to the reduced MSDM, but state transitions were probabilistic. B, p(correct | stage 1) in the deterministic MSDM (single point) and in the five probabilistic MSDM sessions that rats completed. C, p(correct | stage 2) in the deterministic MSDM (single point) and across the five probabilistic MSDM sessions that rats completed. D, Probability of staying with the same first-stage choice based on the previous trial outcome (rewarded vs unrewarded) and the state transition (common: open bars; rare: gray bars) in hypothetical data for a pure model-free agent, a pure model-based agent, or an agent using a mixture of both strategies in the probabilistic MSDM task. E, Probability of staying with the same first-stage choice based on the previous trial outcome (rewarded vs unrewarded) and the state transition (common: blue bars; rare: red bars) in rats (n = 79) during the probabilistic MSDM task reinforced using the alternating schedule. F, Probability of staying with the same first-stage choice based on the previous trial outcome (rewarded vs unrewarded) and the state transition (common: blue bars; rare: red bars) for individual rats in the probabilistic MSDM task reinforced using the alternating schedule. G, Gaussian random walk schedule used to reinforce stage-2 choices in the probabilistic MSDM. H, Probability of staying with the same first-stage choice based on the previous trial outcome (rewarded vs unrewarded) and the state transition (common: blue bars; rare: red bars) in rats (n = 19) using the probabilistic MSDM task that reinforced stage 2 responses using a Gaussian random walk. I, Probability of staying with the same first-stage choice based on the previous trial outcome (rewarded vs unrewarded) and the state transition (common: blue bars; rare: red bars) for individual rats in the probabilistic MSDM task that reinforced stage 2 responses using a Gaussian random walk.