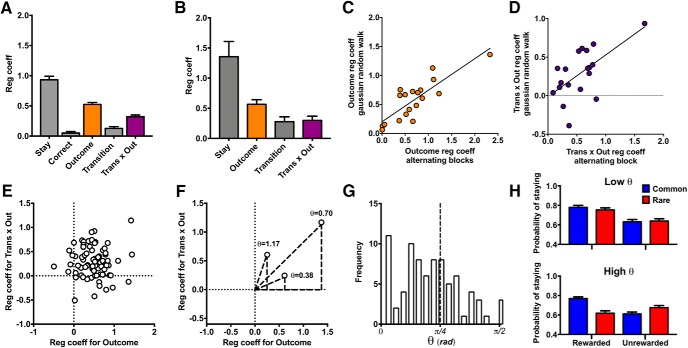
Figure 3.
Characterizing reinforcement-learning strategies in the deterministic MSDM. A, Regression coefficients for predictors in the logistic regression model from choice behavior of rats in the probabilistic MSDM reinforced using the alternating schedule. The coefficient for the outcome predictor (orange bar) represents the strength of model-free learning, whereas the transition-by-outcome interaction predictor (purple bar) represents the strength of model-based learning. B, Regression coefficients for predictors in the logistic regression model from choice behavior of rats in the probabilistic MSDM reinforced stage-2 responses using a Gaussian random walk. C, Relationship between the regression coefficients for outcome predictor estimated from the data collected using the alternating schedule and the Gaussian random walk in the same rats. D, Relationship between the regression coefficients for the transition-by-outcome predictor from the data collected using the alternating schedule or the Gaussian random walk within the same rats. E, Relationship between the outcome and transition-by-outcome regression coefficients within individual rats. F, Angular coordinate (θ, in radians) between the transition-by-outcome and outcome regression coefficients for three rats. A θ value greater than π/4 indicates that the transition-by-outcome weight was higher than that for outcome (e.g., higher model-based learning); a value lower than π/4 indicates that the outcome weight was lower than that for transition-by-outcome (e.g., higher model-free learning). G, Distribution of θ values derived from the logistic regression model. The average θ value was less than π/4 (0.60 +/− 0.03), indicating that the magnitude of model-free learning was higher than that of model-based learning in the probabilistic MSDM task. H, Probability of staying with the same first-stage choice based on previous trial events in rats from the lower (top; n = 20) and upper (bottom; n = 20) quartile of the θ distribution.