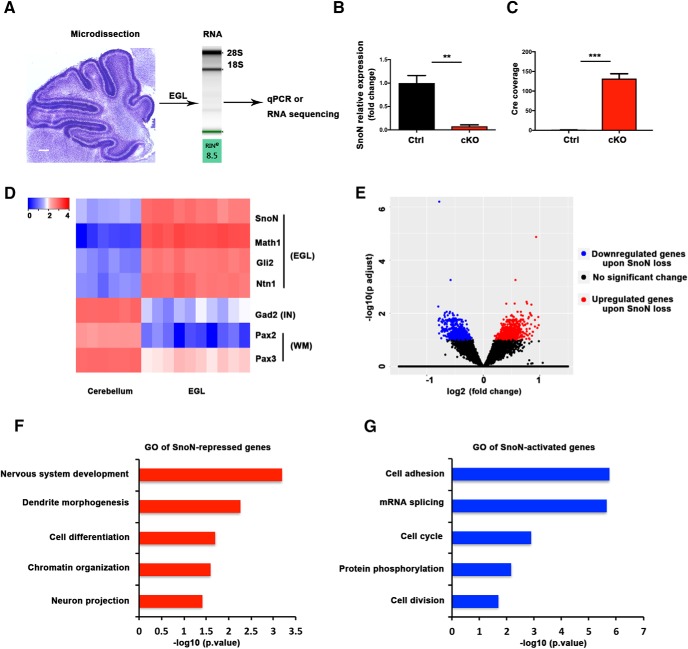
Figure 7.
LCMRNA-seq of the EGL shows that SnoN activates expression of cell proliferation genes and represses neuronal differentiation genes. A, LCM was used to isolate the EGL from the central lobules of control and conditional SnoN KO animals at P6. After BioAnalyzer quality control (Agilent Technologies), intact RNA was used for quantitative PCR analysis or RNA sequencing. Scale bar, 200 μm. B, The EGL from conditional SnoN KO and control littermate mice was subjected to quantitative PCR analysis. SnoN mRNA levels were profoundly lower in the EGL of conditional SnoN KO mice compared with control mice. Graphical data are presented as mean ± SEM. **p < 0.01 (t test). n = 3 mice. C, The recombinase Cre was expressed in the LCM EGL of conditional SnoN KO but not control mice. Graphical data are presented as mean ± SEM. ***p < 0.001 (t test). n = 5 mice. D, RNA-seq analyses of the LCM EGL and whole cerebellum revealed that the EGL genes, Math1, Gli2, and Ntn1, were significantly higher in the EGL compared with whole cerebellum, and genes that are expressed in other region of the cerebellum, such as Gad2 (marker for interneuron [IN]), Pax2 and Pax3 (marker for white matter [WM]) were higher in the whole cerebellum than in the EGL. E, Volcano plot of gene expression changes. The transcriptome of the LCM EGL from conditional SnoN KO mice was compared with that of control mice using DESeq2. The x axis specifies the log2 fold-changes, and the y axis specifies the negative logarithm to the base 10 of the FDR adjusted p values. Red and blue dots represent genes expressed at significantly higher (n = 792) or lower (n = 600) levels upon SnoN loss, respectively (FDR-adjusted p < 0.1). F, Gene ontology analyses of SnoN-repressed genes (i.e., upregulated in the LCM EGL upon conditional SnoN KO) showed gene cluster functions related to neuronal development, cell differentiation, dendrite morphogenesis, and neuron projection. G, Gene ontology analyses of SnoN-activated genes (i.e., downregulated in the LCM EGL upon conditional SnoN KO) showed notable gene cluster functions in cell proliferation, cell adhesion, mRNA splicing, and protein phosphorylation.