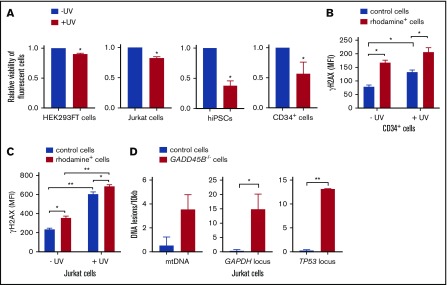
Figure 3.
GADD45B knockout leads to reduced cell viability and increased UV-induced cellular stress. (A) Cell viability of HEK293FT cells, Jurkat cells, iPSCs, and CD34+ HSPCs, transfected with labeled tracr-Cas9 RNP (nontarget RNP) or with labeled GADD45B-targeting CRISPR/Cas9–gRNA RNP, was measured after exposing the cells to UV for 5 minutes, followed by 2 hours of additional incubation. Relative viability of nonirradiated control cells was set as 1.0. (B) CD34+ HSPCs were transfected with fluorescein-labeled GADD45B-targeting CRISPR/Cas9–gRNA RNP. After 48 hours, the cells were exposed to UV irradiation for 5 minutes. Following 2 hours of further incubation, intracellular γH2AX (phospho-Ser139) levels were measured by flow cytometry. (C) Jurkat cells were transfected with CX-rhodamine–labeled GADD45B-targeting CRISPR/Cas9–gRNA RNP. After 48 hours, the total population was exposed to UV irradiation for 5 minutes, followed by 2 hours of incubation before performing intracellular staining and FACS analysis for the DNA damage marker γH2AX (phospho-Ser139). (D) mtDNA damage (left panel) and nuclear DNA damage in the GAPDH locus (middle panel) and TP53 locus (right panel) were quantified in Jurkat control cells and a GADD45B−/− Jurkat clone using the LORD-Q method. Data are mean ± standard deviation from 3 (A-B) or 2 (C-D) independent experiments, each performed in duplicates. *P ≤ .05, **P ≤ .01, Student t test.