Figure 1.
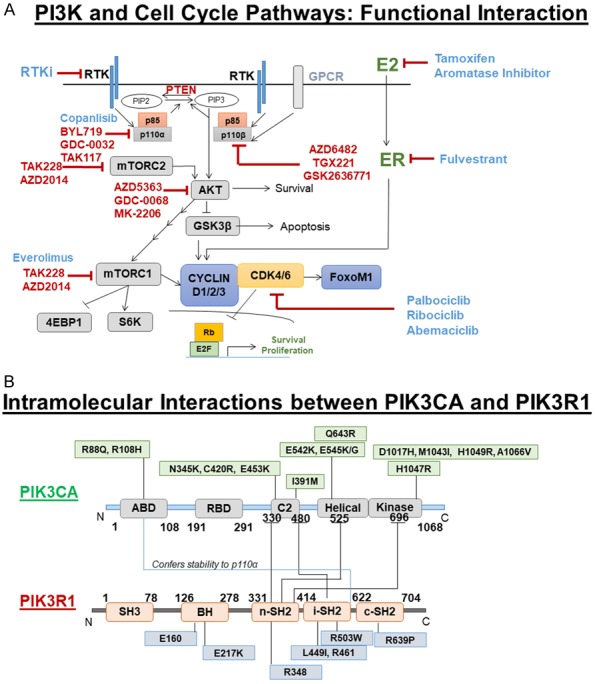
A. The Mechanistic relationship between PI3K pathway activation and cell-cycle in tumor cells: PI3K signaling engages AKT, which drives mTORC1 CAP-dependent mRNA translation encoding CYCLIN D1/D2/D3. CYCLIN D1/D2/D3 bind CDK4/6 to promote RB phosphorylation, which depresses E2F transcription factor to drive expression of genes that promote proliferation and suppress apoptosis. CDK6 can phosphorylate FOXOM1 to enhance FOXOM1 stability, which suppresses senescence. Blue: FDA approved drugs and RED: Active in a clinical trial. B. Intramolecular interactions between PIK3CA and PIK3R1: Domain-specific regulation of PIK3CA (a p110α catalytic subunit of PI3K) by PIK3R1 (p85α regulatory subunit of PI3K) as scaffolds for regulated complex formation. Distribution of some important non-synonymous mutations of PIK3CA and PIK3R1 were depicted.
