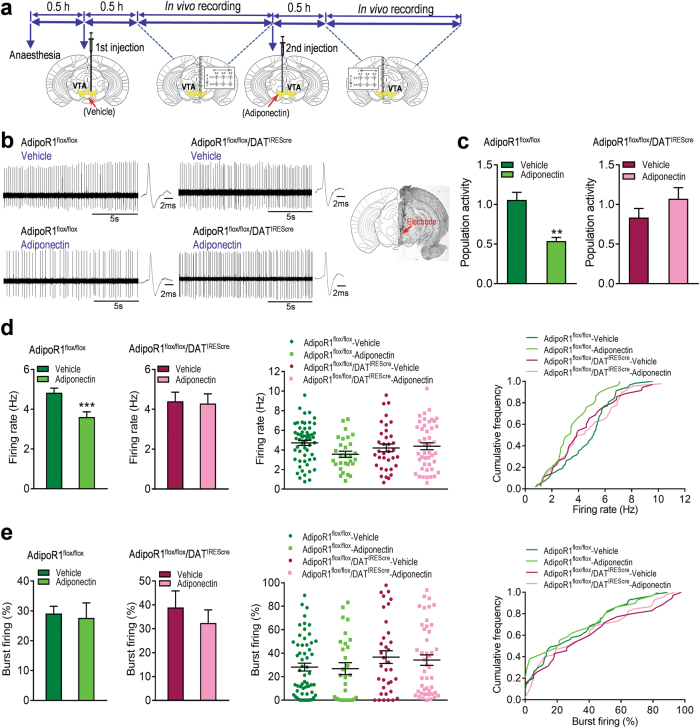
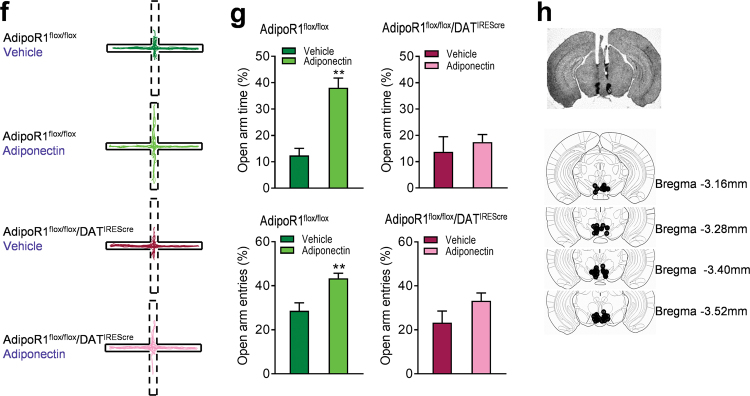
Fig. 5.
AdipoR1 mediates the effects of adiponectin on VTA dopamine neuron activity and anxiety-like behavior. (a) Schematic procedure of in vivo extracellular recording of dopamine neurons in the VTA. (b) Left, representative extracellular voltage traces from VTA dopamine neurons; right, representative image demonstrating the electrode track through the VTA. (c) Number of spontaneously active dopamine neurons per track in the VTA. (d) Left and middle-left, firing rate; middle-right, scatter plot distribution; right, cumulative frequency distribution. (e) Left and middle-left, percentage of burst firing; middle-right, scatter plot distribution; right, cumulative frequency distribution. AdipoR1flox/flox + vehicle: n = 9 mice, AdipoR1flox/flox + adiponectin: n = 9 mice, AdipoR1flox/flox/DATIREScre + vehicle: n = 7 mice; AdipoR1flox/flox/DATIREScre + Adiponectin: n = 7 mice. (f) Representative traces of the elevated plus maze test in four different treatment groups. (g) Top, percentage of open/total arm time; bottom, percentage of open/total arm entries. (h) Top, representative picture showing injection sites; bottom, schematic diagram of injection sites in the VTA. AdipoR1flox/flox + vehicle: n = 7 mice; AdipoR1flox/flox + adiponectin: n = 6 mice; AdipoR1flox/flox/DATIREScre + vehicle: n = 6 mice; AdipoR1flox/flox/DATIREScre + Adiponectin: n = 7 mice. **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001 compared with the vehicle-treated mice