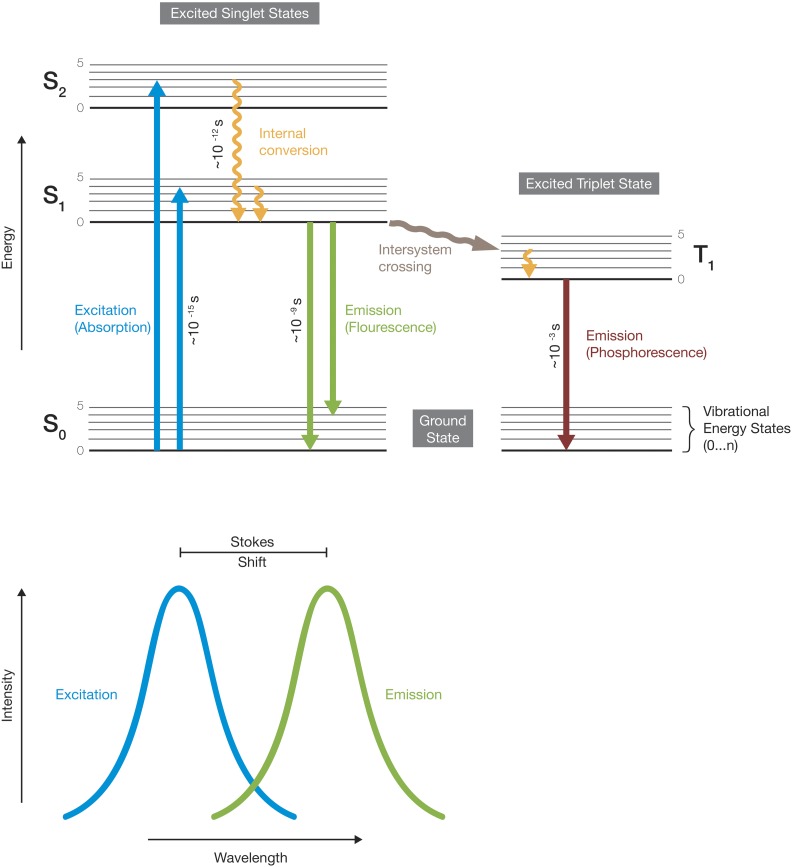
Figure 1.
Principles of fluorescence. The Jablonski energy diagram illustrates the electronic states of a fluorophore and the transitions between them. Electronic states are indicated by horizontal lines, whereby thick lines depict the respective vibrational ground states. The transitions within and between electronic states can be nonradiative (wiggly arrows) or radiative (straight arrows), and occur at different timescales. When excited electrons return to their ground state at a nanosecond-scale, they emit fluorescence. The emission of fluorescence signals generally occurs at a longer wavelength. The shift between excitation and emission wavelengths is termed Stokes shift. S0, ground state; S1 or S2, higher electronic singlet energy states; T1, triplet energy state.