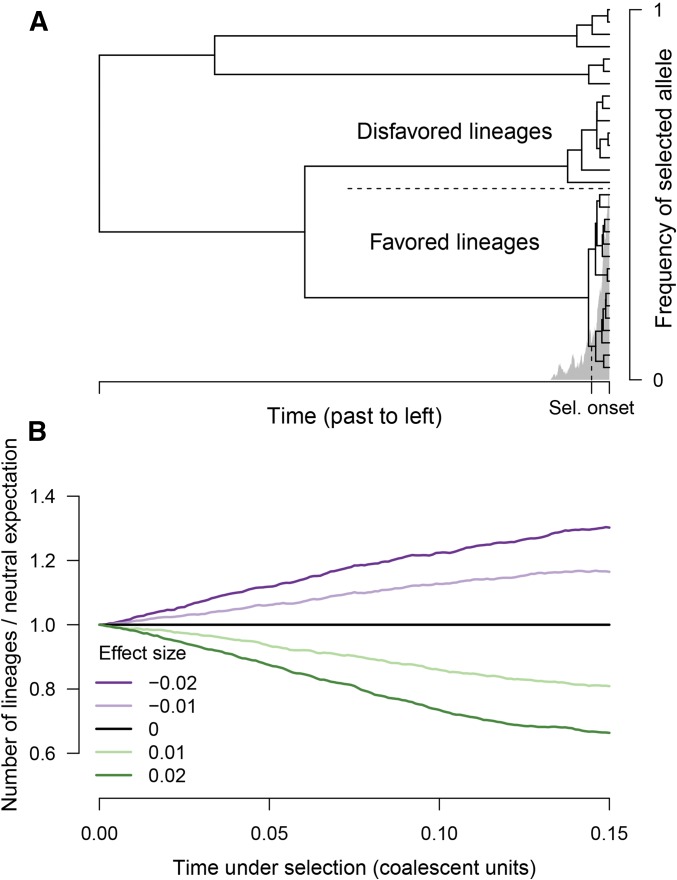
Figure 1.
Selection distorts the coalescent tree at a locus. (A) The frequency time course for an allele that has been favored by recent selection is shown in gray. Superimposed is a coalescent tree relating a sample of chromosomes; the top half are of the disfavored type, and the bottom half are of the favored type. Because the favored alleles trace to a pool of ancestors that was small before selection, there is an excess of recent coalescence on the subtree of the favored allele. (B) If a polygenic trait is under directional selection, the rate of coalescence depends on effect size. The time under selection is shown on the horizontal axis, and the vertical axis shows the ratio of lineages remaining compared with the neutral expectation. Different lines show different effect sizes in units of trait standard deviation. Results are an average across 1000 simulations; selection coefficients are determined as if the trait experiences 1% directional truncation selection. Sel., selection.