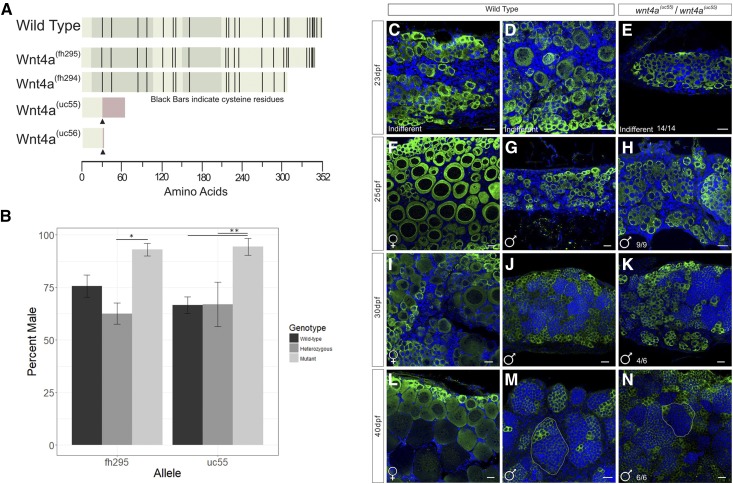
Figure 3.
Mutant wnt4a alleles result in male-biased populations. (A) Wnt4a is a 352 amino acid protein with five exons, indicated by the alternating shaded regions. Protein structures predicted to arise from each allele are indicated by truncation, wnt4a(fh295/fh294) (ENU-induced mutation), or insertion (CRISPR, ▴) resulting in missense protein coding (red bar) in uc55/uc56. (B) Sex ratios in populations of homozygous wnt4a(fh295) and wnt4a(uc55) mutants were significantly male biased by ANOVA. * P < 0.05, ** P < 0.01, n = 3 replicates. Comparison of (C, D, F, G, I, J, L, and M) representative wild-type and (E, H, K, and N) wnt4a mutant gonads stained for Vasa, to identify germ cells (green), and DAPI, to label nuclei (blue), at various ages postfertilization (dpf). At 23 dpf, (E) wnt4a mutants and (C and D) wild types both have indifferent gonad morphology. In contrast, the majority of wnt4a mutant gonads from 25 dpf animals and older (H, K and N) had a morphology that is indistinguishable of wild-type testes (G, J and M), but not wild-type ovaries (F, I and L). Bar, 20µm.