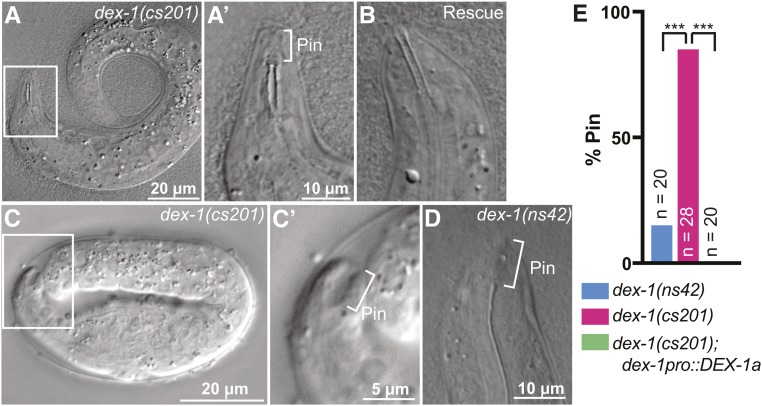
Figure 4.
dex-1 mutants are Pin (pharynx ingressed). (A) dex-1(cs201) L1 larva. Box indicates region that will be magnified in subsequent panel. (A’) The pharynx opening was posterior to the nose tip (bracket) and presumably did not open to the outside environment. (B) dex-1 cDNA efficiently rescued the pharyngeal phenotype. (C) twofold dex-1 mutant embryo. (C’) The pharynx was ingressed (bracket) but attached to the nose tip epithelium, leaving a large “keyhole” indicative of a true Pin phenotype (Kelley et al. 2015). (D) The Pin phenotype was also observed in dex-1(ns42) mutants. (E) Quantification of frequency of Pin phenotype in newly hatched L1 larvae. *** P < 0.0001, Fisher’s exact test.