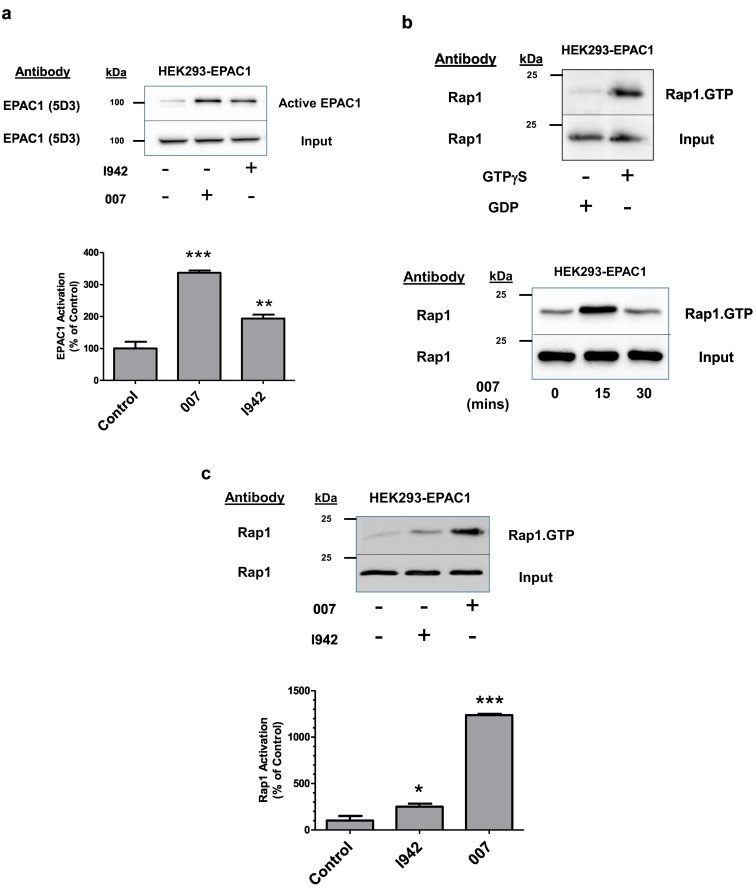
Fig. 1.
The novel EPAC1 ligand, I942, activates EPAC1 and Rap1 in HEK293T cells.
a) EPAC1-expressing HEK293TT (HEK293T-EPAC1) cells were incubated with either I942 (100 μM) or 007 (50 μM) for 30 min and then cell extracts were immunoprecipitated with the anti-EPAC1 antibody, 5D3, which selectively interacts with the active form of EPAC1. The amount of immunoprecipitated, active EPAC1 in cell extracts was determined by western blotting with the 5D3 antibody (upper panel), with increased EPAC1 immunoreactivity indicating an increase in cellular EPAC1 activation. Multiple western blots were analysed by densitometry and the results are displayed as a histogram of means ± S.E.M. in the lower panel. Significant increases in EPAC1 activity, relative to diluent-treated control cells, are indicated; **, p < 0.01 and ***, p < 0.001, respectively (n = 3).
b) Active Rap1 was isolated from HEK293T-EPAC1 cell extracts stimulated with either GDP or GTPγS using affinity purification columns as described in Materials and methods. The amount of purified active Rap1 in stimulated samples was determined by western blotting with an anti-Rap1 antibody (upper panel). In the lower panel, HEK293T-EPAC1 cells were stimulated for the indicated time with 007 (50 μM) and then active, Rap1.GTP, was isolated from cell extracts as described in Materials and methods.
c) HEK293T-EPAC1 cells were incubated with either I942 (100 μM) or 007 (50 μM) for 30 min and then Rap1.GTP was isolated from cell extracts using affinity purification columns and visualised by immunoblotting with an anti-Rap1 antibody as described in Materials and methods. Multiple western blots were analysed by densitometry and the results are displayed as a histogram of means ± S.E.M. in the lower panel. Significant increases in Rap1 activity, relative to diluent-treated control cells, are indicated; *, p < 0.05 and ***, p < 0.001, respectively (n = 4).